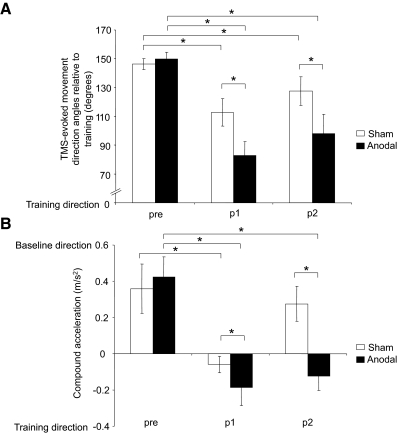
FIG. 4.
Angular distance and compound acceleration of TMS-evoked movements. A: angular distance of TMS-evoked movements relative to training during pre, p1, and p2. In comparison to sham, anodal tDCS led to a greater reduction in the angular distance between training movements and those evoked by TMS at p1 and p2 times. Please note that at pre, both sessions have similar angular difference from the trained direction. B: average compound acceleration during pre, p1, and p2. Anodal tDCS led to a greater change in direction of compound acceleration during p1 and p2 relative to sham. Asterisks, P ≤ 0.03. Data are means ± SE.