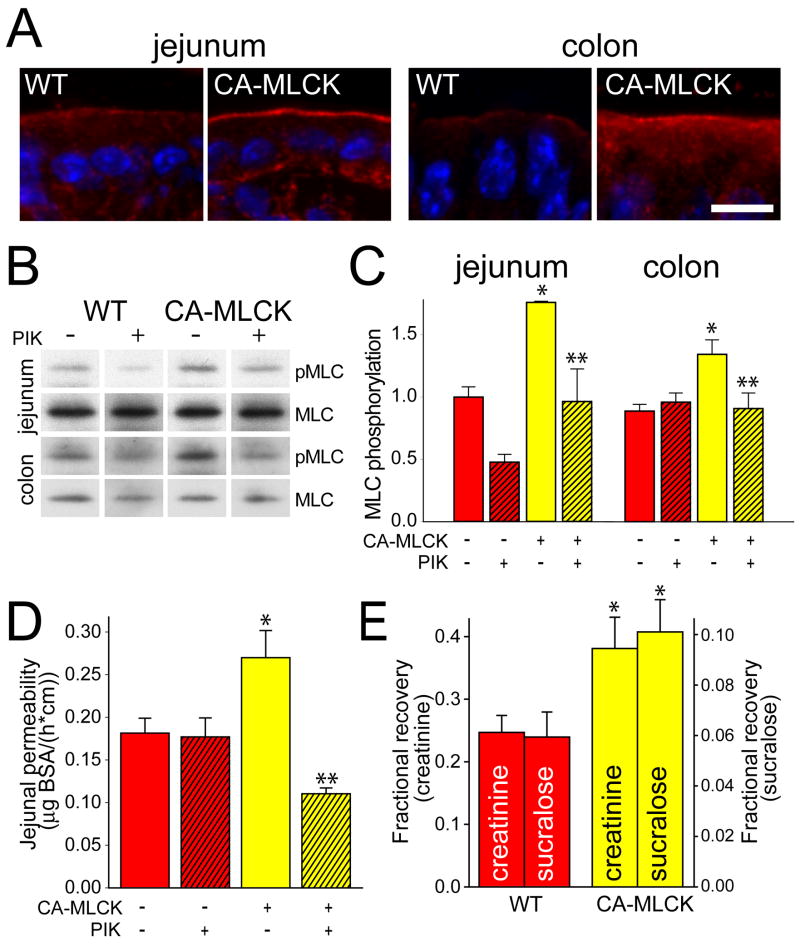
Figure 2. CA-MLCK expression causes increas ed intestinal epithelial MLC phosphorylation and intestinal barrier loss.
(A) Phosphorylated MLC (red) in jejunum and colon of WT and CA-MLCK Tg mice. Nuclei are shown in blue. Bar, 10 μm. (B, C) Immunoblot of phosphorylated MLC (pMLC) and total MLC and densitometric analysis of WT (red bars) and CA-MLCK Tg (yellow bars) after in vivo perfusion with (hatched bars) or without (solid bars) PIK. n=4 for each condition. *, P<0.01 vs. WT littermates; **, P<0.05 vs. CA-MLCK Tg mice without PIK. (D) Paracellular BSA flux with or without PIK. n=4 for each condition. *, P<0.01 vs. WT; **, P<0.01 vs. Tg without PIK.(E) In vivo measurement of colonic paracellular permeability in WT and CA-MLCK Tg mice. *, P<0.02 vs. WT.