Abstract
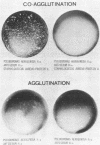
Antisera against the two major flagellar antigens of Pseudomonas aeruginosa were obtained by immunization of rabbits with isolated flagella and absorption of contaminating antisomatic antibodies. In the conventional slide agglutination test, the pure H antisera did not agglutinate the flagellated cells of the homologous strains. The addition of protein A-bearing staphylococci to H antiserum and homologous flagellated cells, the so-called slide coagglutination, results in a rapid development of flaky clumps. H coagglutination tests of reference strains, which formerly have been H typed by long-term tube agglutination and by the indirect fluorescent-antibody technique, yielded exactly the same subdivision of the strains in H type a and H type b as the more laborious and time-consuming methods. O grouping and H typing of 181 isolates from clinical specimens revealed a free combination of the somatic and flagellar antigens. 25 OH serovars were found. The simple and rapid coagglutination technique can promote the serovar determination of P. aeruginosa, particularly for the purpose of hospital infection control.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ansorg R. Flagellaspezifisches H-Antigenschema von Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Zentralbl Bakteriol Orig A. 1978 Nov;242(2):228–238. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ansorg R., Fraatz G., Strempel D. Isolierung, Depolymerisierung und Repolymerisierung der Geisseln von Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Zentralbl Bakteriol A. 1980 Mar;246(3):363–372. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ansorg R., Schmitt W., Schwerk V. Antikörperbildung gegen somatische und flagelläre Antigene von Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Med Microbiol Immunol. 1978 Oct 20;165(3):181–189. doi: 10.1007/BF02123175. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ansorg R., Weber R., Kleinmaier H. Untersuchungen zur serologischen Typisierung von Pseudomonas aeruginosa mit der indirekten Immunofluoreszenztechnik. Zentralbl Bakteriol Orig A. 1977;237(2-3):280–296. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holder I. A., Wheeler R., Montie T. C. Flagellar preparations from Pseudomonas aeruginosa: animal protection studies. Infect Immun. 1982 Jan;35(1):276–280. doi: 10.1128/iai.35.1.276-280.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kronvall G. A rapid slide-agglutination method for typing pneumococci by means of specific antibody adsorbed to protein A-containing staphylococci. J Med Microbiol. 1973 May;6(2):187–190. doi: 10.1099/00222615-6-2-187. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lányi B. Serological properties of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. II. Type-specific thermolabile (flagellar) antigens. Acta Microbiol Acad Sci Hung. 1970;17(1):35–48. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montie T. C., Craven R. C., Holder I. A. Flagellar preparations from Pseudomonas aeruginosa: isolation and characterization. Infect Immun. 1982 Jan;35(1):281–288. doi: 10.1128/iai.35.1.281-288.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pitt T. L., Bradley D. E. The antibody response to the flagella of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Med Microbiol. 1975 Feb;8(1):97–106. doi: 10.1099/00222615-8-1-97. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]