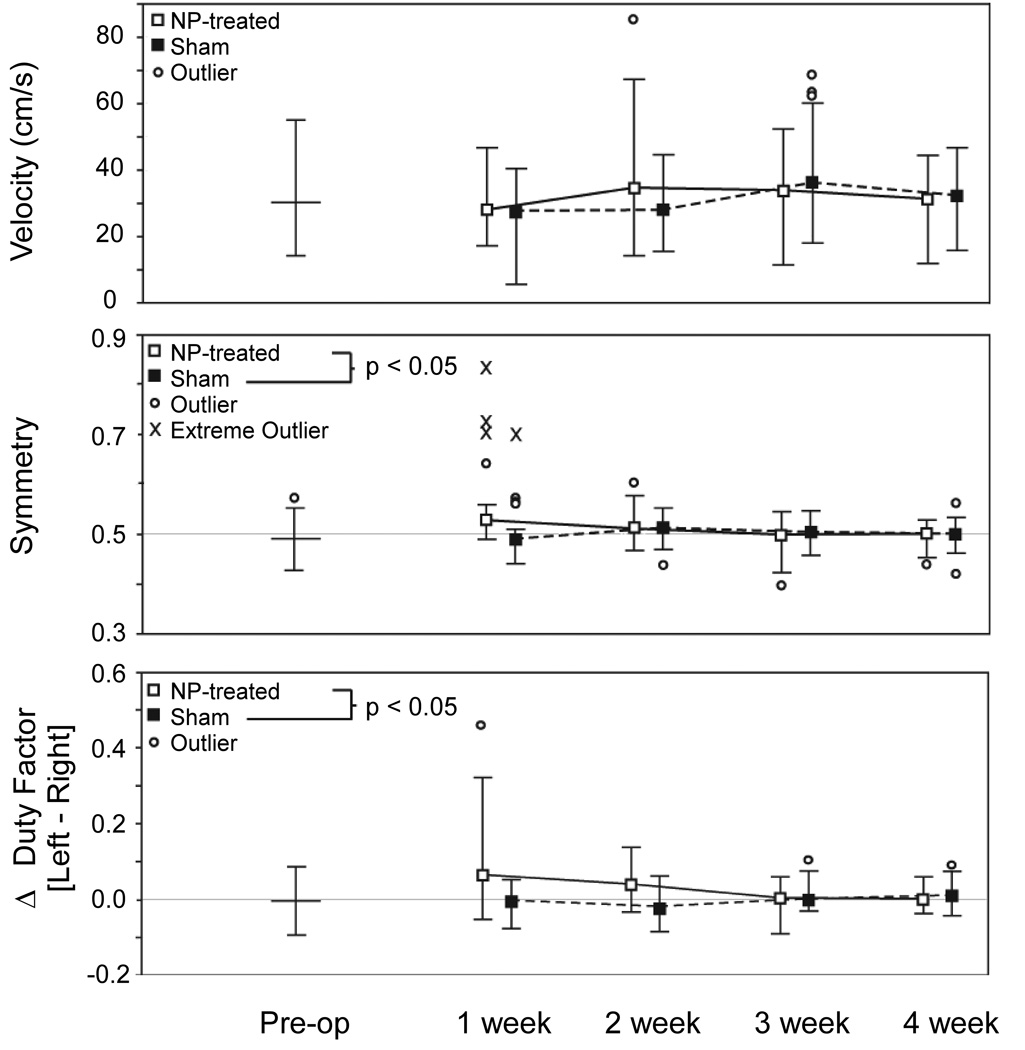
Figure 2.
Analysis of gait parameters are shown for velocity (upper panel), symmetry (middle panel), and Δ duty factor (lower panel). Data for NP-treated animals (white) and sham animals (black) are presented as median whisker plots of the non-outlier range for 4 animals per group with 4 and 7 successful trials per animal. No difference between treatment groups was observed for animal velocity (p = 0.35). Animals in the NP-treated group had early gait asymmetry compared to sham animals (p < 0.05), with the magnitude decreaseing over time (p < 0.01). Animals in the NP-treated group also spent more time on their contralateral limb, especially at early time points, reflected in an imbalance in duty factor (ΔDF, p < 0.001). These differences also decreased in magnitude over time (p < 0.001).