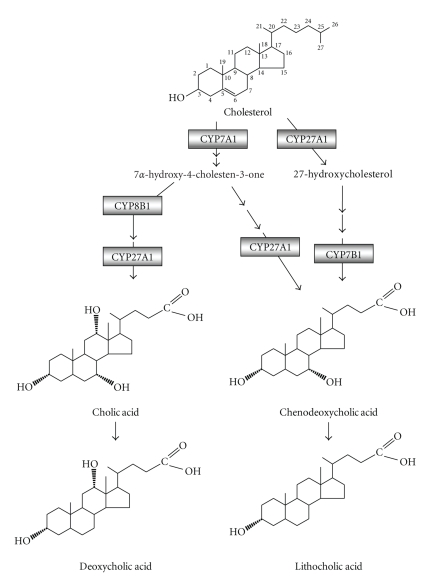
Figure 1.
Bile acid synthesis. Bile acids are synthesized from cholesterol in the liver through two pathways: the classic pathway and the alternative pathway. In human liver, bile acid synthesis mainly produces two primary bile acids, cholic acid (CA), and chenodeoxycholic acid (CDCA). Key regulatory enzymes in both pathways are indicated. CYP7A1 catalyzes the first the rate-limiting step in the classic pathway to convert cholesterol into 7α-hydroxycholesterol, while CYP27A1 initiates the alternative pathway by converting cholesterol into 27-hydroxycholesterol, which is then 7α-hydroxylated by oxysterol 7α-hydroxylase (CYP7B1). CYP8B1 regulates the cholic acid synthesis in the classic pathway. In the intestine, primary bile acid CA and CDCA are dehydroxylated at the 7α-position by the bacterial enzymes to produce the secondary bile acids, deoxycholic acid (DCA), and lithocholic acid (LCA), respectively.