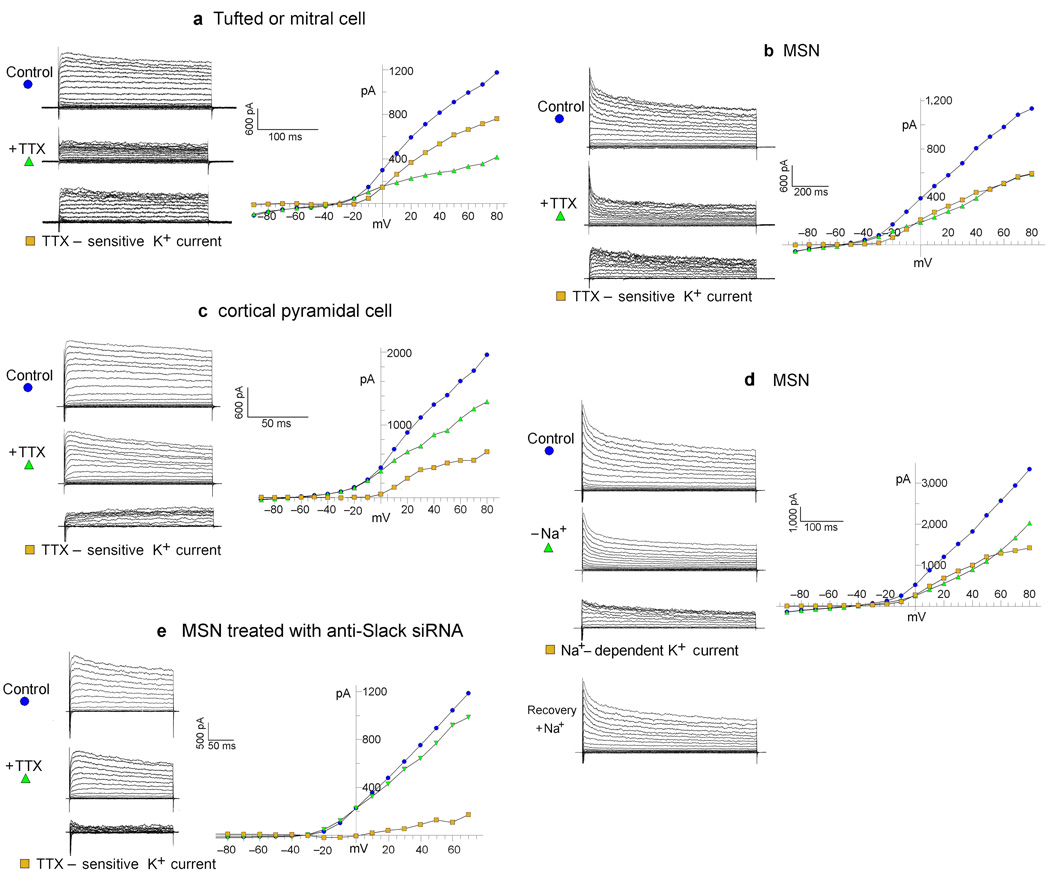
Figure 1. The TTX-sensitive (Na+-dependent) delayed outward current, and its elimination by anti-Slack siRNA.
( See Figure 2 for statistical analysis). a, b, c, The TTX-sensitive delayed outward current in tufted/mitral cell, MSN, and cortical pyramidal cell, respectively. Top traces show the family of control currents evoked from a holding potential of −70 mV. Middle traces show the outward current remaining after addition of TTX (1µM). Bottom traces show the TTX-sensitive current (TTX-sensitive K+ current) which is the difference between the control currents before TTX, and the remaining currents after the addition of TTX. The current values shown in the I/V plots to the right were average values measured within the interval of 150 to 250 ms after the initiation of the voltage step. The intracellular pipette solution in these whole cell patch clamp experiments contained no Na+. Also, Ca2+ was not present in the extracellular recording solutions. See text and Figure 2 for statistics. Some current traces in our experiments show unusual kinetics at the initiation of the voltage clamp step pulse. It is likely that these are anomalies due to the fact that TTX is not present, and therefore very rapid inward Na+ currents are opposing rapid transient outward currents at the initiation of the pulse, in a cell where the space clamp is not perfect (which is why TTX is so often used in studies of outward currents). d. The removal and subsequent replacement of extracellular Na+ shows the Na+-dependent delayed K+ current in a MSN. Control: the family of control currents evoked from a holding potential of −70 mV. −Na+: the outward current remaining after removal of external Na+. Na+-dependent K+ current: the difference between the control currents before Na+ removal and the remaining currents after Na+ removal. Recovery: the current after reintroduction of extracellular Na+ (see Figure 2 for statistics). The intracellular pipette solution in these whole cell patch clamp experiments contained no Na+. e. An example of an MSN treated with Slack-siRNA having a smaller TTX-sensitive outward component. Experiments like these support the hypothesis that the TTX-sensitive delayed outward current is carried by Slack channels (See Figure 2 for statistics). Composition of recording solutions (in mM): Bath Solution (NaCl 150, KCl 5, MgCl2 2, Dextrose 10, HEPES 10, pH 7.4 with NaOH); 0 Na+Bath Solution (CholineCl 150, KCl 5, MgCl2 2, Dextrose 10, HEPES 10, pH 7.4 with KOH).; Pipette Solution ( KCl 150, HEPES 10, EGTA 5, CaCl2 1, pH to 7.4 with KOH).