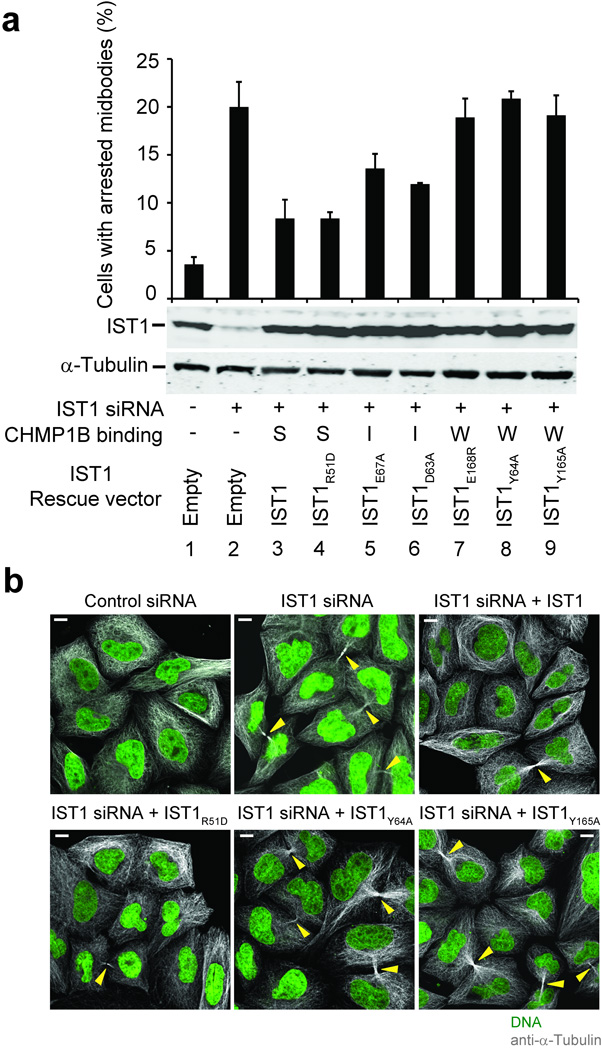
Figure 5.
Requirement for IST1-CHMP1 interactions during abscission. (a) The upper panel shows quantified abscission defects as reflected in the percentages of HeLa M cells with visible midbodies following siRNA treatment to deplete endogenous IST1 (lanes 2–9) and rescue with an empty vector control (lane 2, negative control) or with vectors expressing wild type IST1 (lane 3, positive control) or the designated IST1 mutants (lanes 4–9). Untreated cells are shown in lane 1. Error bars show standard deviations from three independent repetitions of the experiment. The middle panel is a western blot (anti-IST1) showing levels of soluble endogenous IST1 (lanes 1 and 2) or exogenously expressed IST1 proteins (lanes 3–9). The bottom panel is a western blot (anti-α-Tubulin) showing expression levels of endogenous α-Tubulin (loading control). CHMP1B binding phenotypes of the different IST1 proteins are shown below: strong (S), intermediate (I), or weak (W). (b) Immunofluorescence images showing the midbody phenotypes of cells from a designated subset of the experiments from a. Microtubules (anti-α-Tubulin, grey) and nuclei (SYTOX green) were stained for reference, and yellow arrowheads highlight midbodies. Scale bars are 10µm.