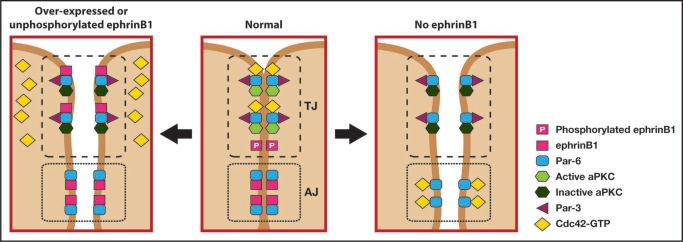
Figure 1.
EphrinB1 regulates tight junction formation through an interaction with Par-6. Unphosphorylated ephrinB1 may compete with Cdc42-GTP for Par-6 binding and inhibit aPKC activation in the Par complex, leading to tight junction disruption (left panel). Upon tyrosine phosphorylation ephrinB1 fails to interact with Par-6, which is now available to interact with Cdc42-GTP and establish tight junctions (middle panel). Loss of ephrinB1 may allow Par-6 that is localized at adherens junctions and lateral cell borders compete with tight junction-associated Par-6 for Cdc42-GTP. The resulting reduction in Cdc42-GTP localized at the apical border may reduce aPKC activity and disrupt tight junctions (right panel).