Figure 5.
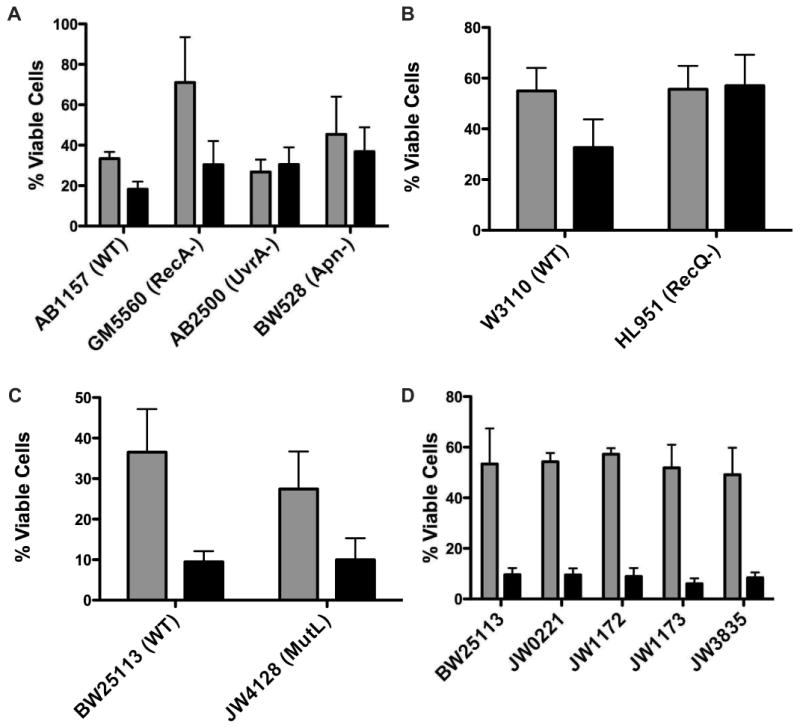
Bacterial Cytotoxicity of DNA Repair and Bypass Polymerase Deficient Strains. Gray bars report bacterial growth after exposure to 0.5 mM CTP-Cl while black bars report growth after exposure to 2.5 mM TPP-Br. Results are mean values of three independent experiments with standard error indicated. (A) AB1157 is parental strain for GM5560, AB2500 and BW528. GM5560 is deficient in recA, a critical Homologous Recombination repair pathway protein. AB2500 contains three mutations (uvrA, thyA and deoB) rendering these cells deficient in Nucleotide Excision Repair. BW528 has the two AP endonucleases, nth and xfo, deleted making this strain deficient in Base Excision Repair. (B) W3110 serves as parent strain for deletion of the replication fork stall stabilizing protein recQ (HL951). (C) BW25113 is parent strain for JW4128 that is deficient in mismatch repair (mutL). (D) Strains were obtained from Yale E. Coli database (Keio Collection) with single deletions as follows: BW25113, Parental strain; JW0221, dinB deficient; JW1172, umuC deficient; JW1173, umuD deficient and JW3835, polA deficient. Results are the mean values of three independent experiments with standard deviations indicated.
