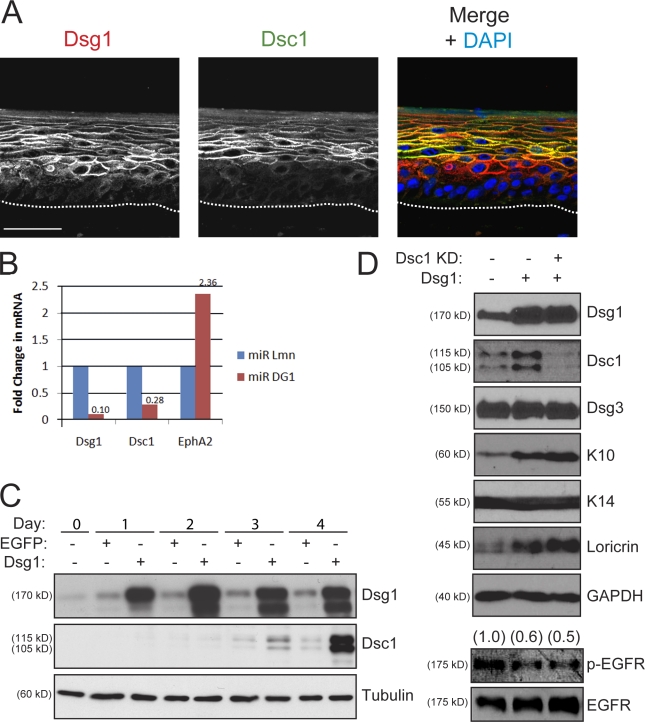
Figure 5.
Dsg1 promotes keratinocyte differentiation in a manner that does not rely on its regulation of Dsc1 expression. (A) Dual-label IHC staining revealed that Dsg1 (red) is expressed in lower cellular layers of day 6 rafts compared with Dsc1 (green). A merged overlay image containing DAPI (blue) as a nuclear stain is mounted to the right. The dotted lines indicate the boundary between keratinocytes and the collagen matrix. (B) Real-time PCR analysis showed that Dsc1 mRNA levels are reduced in Dsg1 knockdown rafts. The mRNA levels of Dsg1, Dsc1, and a gene target of EGFR, EphA2, were normalized to 18-S ribosomal RNA using the comparative CT method. The data are representative of four independent experiments and are shown as fold change from miR Lmn controls. (C) Ectopic Dsg1-Flag in keratinocytes maintained in low (0.2 mM) Ca2+ to limit differentiation results in a time-dependent increase in Dsc1 expression compared with EGFP-transduced controls. Protein lysates from 0 to 4 d after retroviral transduction were analyzed using an antibody specific for Dsg1 (ectopic + endogenous), Dsc1, or tubulin as a loading control. (D) Dsg1-Flag was ectopically expressed in keratinocytes and additionally transfected with a pool of Dsc1 siRNA or control oligonucleotides (75 nM total) for 48 h in low Ca2+. Confluent cultures were switched into high (1.8 mM) Ca2+ to initiate differentiation and harvested after 24 h. Ectopic Dsg1 was capable of increasing the levels of differentiation-associated proteins, whereas the levels of p-EGFR were reduced. Dsc1 knockdown (KD) did not interfere with the Dsg1-dependent changes in K10, loricrin, or p-EGFR. Ratios of p-EGFR to total EGFR are indicated above the blots. GAPDH, glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase. Bar, 50 µm.