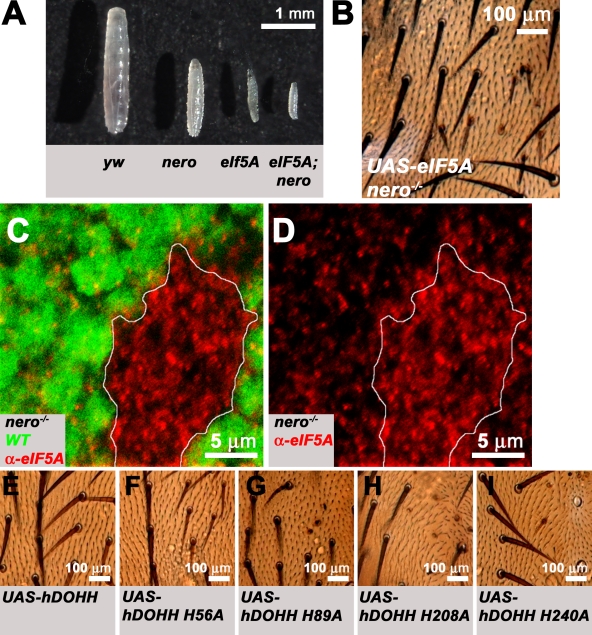
Figure 7.
nero regulates eIF5A levels in vivo and Nero's DOHH activity is required for nero function. (A) Synchronized larvae 72 h after egg hatching of four different genotypes (from left to right): y w, nero1, eIF5AP01296, and eIF5AP01296; nero1. The growth of eIF5AP01296; nero1 double mutant larvae appears to be more impaired than either eIF5AP01296 or nero1 homozygous mutant larvae. (B) Overexpression of eIF5A in nero mutant clones fails to rescue bristle growth defects associated with nero mutant clones (genotype: y w hs-FLP tub-GAL4 UAS-GFP-6xMYC-NLS/+; UAS-eIF5A/+; FRT82B nero1/FRT82B hsp70-CD2 y+ tub-GAL80). (C and D) eIF5A levels are dramatically up-regulated in nero mutant clones in the wing imaginal disc. nero mutant clones are marked by the absence of GFP (green; genotype: y w hs-FLP; FRT82B nero1/FRT82B Ubi-GFP). White lines mark the clonal boundary. WT, wild type. (E) Overexpression of hDOHH in nero mutant clones rescues bristle size defects (genotype: y w hs-FLP tub-GAL4 UAS-GFP-6xMYC-NLS/+; UAS-hDOHH/+; FRT82B nero1/FRT82B hsp70-CD2 y+ tub-GAL80). (F–I) Overexpression of mutated forms of hDOHH in nero mutant clones fails to rescue bristle size defects. Genotypes are essentially identical to E except mutated forms of hDOHH are expressed under the UAS regulation. (F) Genotype: y w hs-FLP tub-GAL4 UAS-GFP-6xMYC-NLS/+; UAS-DOHH H56A/+; FRT82B nero1/FRT82B hsp70-CD2 y+ tub-GAL80. (G) Genotype: y w hs-FLP tub-GAL4 UAS-GFP-6xMYC-NLS/+; UAS-hDOHH H89A/+; FRT82B nero1/FRT82B hsp70-CD2 y+ tub-GAL80. (H) Genotype: y w hs-FLP tub-GAL4 UAS-GFP-6xMYC-NLS/+; UAS-hDOHH H208A/+; FRT82B nero1/FRT82B hsp70-CD2 y+ tub-GAL80. (I) Genotype: y w hs-FLP tub-GAL4 UAS-GFP-6xMYC-NLS/+; UAS-hDOHH H240A/+; FRT82B nero1/FRT82B hsp70-CD2 y+ tub-GAL80. (B and E–I) Mutant bristles are marked by the recessive yellow mutation and appear light brown.