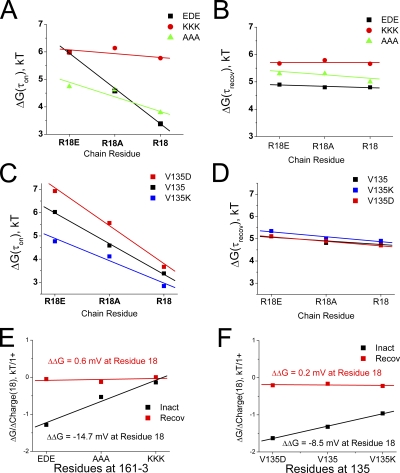
Figure 9.
Analysis of the importance of electrostatics for interactions between residue 18 and the side window residues 161–3 and 135. Charge-changing mutations were made in both the side window location and in residue 18, and the energetic effect on the rate-limiting inactivation ON and recovery reactions was determined. (A) Changing residue 18 charge alters the energetics of the inactivation on reaction in a linear manner. The slope changes depending on the charge present at residues 161–3. As 161–3 is made more positive, the energetic impact of changing residue 18 charge is lost, indicating a large electrostatic contribution of 161–3 on the potential change felt by residue 18. (B) There is little impact on recovery of charge changes to residue 18, and the slopes of these lines do not change much with changes in the charge at residues 161–3. (C) Charge at residue 135 has a similar effect on slope as residue 161–3, but the impact is less pronounced. Because residue135 is at the axis of symmetry, four net charges in the center of the side windows are changed with each residue 135 mutation; however, the number of these charges that are seen by residue 18 is unknown. (D) As expected, energetic coupling shows little charge dependence for residue 18 and 135 between the bound and transition state during recovery. (E) Summary diagram for coupling between residue 18 and 161–3. As expected, there is no significant change in electrostatic interaction between residue 18 and 161–3 during the recovery process, but there is a large potential change produced during inactivation as the polar region binds. The potential produced by EDE(161–3) is ∼−15 mV, about half the total potential change seen by residue 18. (F) Coupling between residue 18 and 135 shows a similar pattern with no change in interaction during recovery, but an estimated −8.5-mV change on binding (with V135D). Because curves are almost perfectly linear, it suggests that there is no significant non-electrostatic interaction between residue 18 and residue 135. Because residue 135 is normally uncharged, this interaction has no impact on inactivation in the wild-type channel.