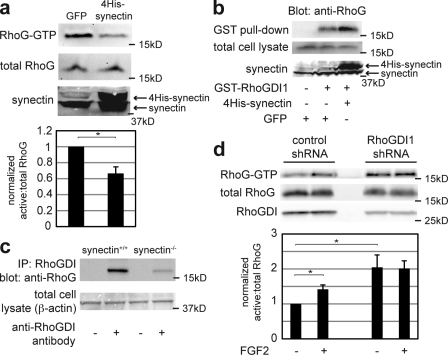
Figure 3.
Synectin and RhoGDI1 are required for RhoG suppression at baseline. (a) WT murine pulmonary microvascular endothelial cells were transfected with either GFP- or 4His-tagged synectin 48 h before lysis and RhoG activity assay. Cells were serum starved in 0.5% FBS/DME for 24 h before lysis. (bottom) Quantification from three experiments is shown. *, P = 0.052. (b) Mock-transfected RFPECs (left and middle) and those transfected with 4His-tagged synectin (right) were lysed 48 h after transfection. Pull-downs were performed using glutathione beads conjugated with GST-RhoGDI1 (middle and right) or glutathione beads alone (right). (c) Lysates from WT and synectin knockout murine pulmonary microvascular endothelial cells were normalized to equal protein concentrations and incubated with monoclonal anti-RhoGDI antibodies and protein A/G beads (+) or beads alone (−). After washing and protein elution, the samples were analyzed by SDS-PAGE and probed with an anti-RhoG antibody. IP, immunoprecipitation. (d) RFPECs were transfected with a control shRNA sequence or shRNA specific for RhoGDI1. 24 h after transfection, cells were placed in 0.5% FBS/DME for an additional 24 h, at which time they were lysed and assayed for RhoG activity. The quantifications show the mean of three experiments and reveal a more than twofold increase in baseline RhoG activity in cells treated with RhoGDI1 shRNA. * (bottom to top), P = 0.034 and 0.008. Error bars indicate SEM.