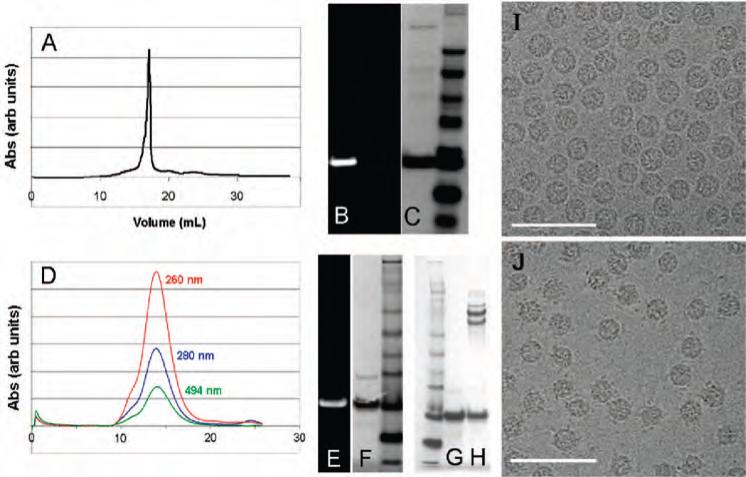
Figure 6.
Characterization of virus-like capsids after CuAAC reactions: HBV = A-C; Qβ = D-H. (A) Size exclusion chromatography showing a peak with a retention volume of 18 mL corresponding to disassembled capsid. (B,C) SDS-PAGE of the Cp149 protein isolated from the reaction, visualized under ultraviolet illumination (B) and then with Coumassie staining (C). The right lane is a molecular weight ladder. (D) Size exclusion chromatography showing an elution volume of 14 mL, characteristic of intact Qβ capsids, and coelution of fluorescein with the protein showing covalent attachment. (E,F) SDS-PAGE of the Qβ protein showing fluorescein labeling as above. (G) Same as (F). (H) SDS-PAGE of purified Qβ-transferrin conjugate; the higher molecular weight bands are in the expected position for the Cp149-transferrin fusion, with multiple bands deriving from the somewhat impure nature of the starting transferrin sample. (I) Transmission electron microscopy (TEM) image of Qβ (1MN3)9−18(K16M-N3)180. (J) TEM image of the same particle conjugated to transferrin-alkyne 9, after purification. Note the appearance of spots surrounding most of the particles, due to the tethered 80 kD protein.