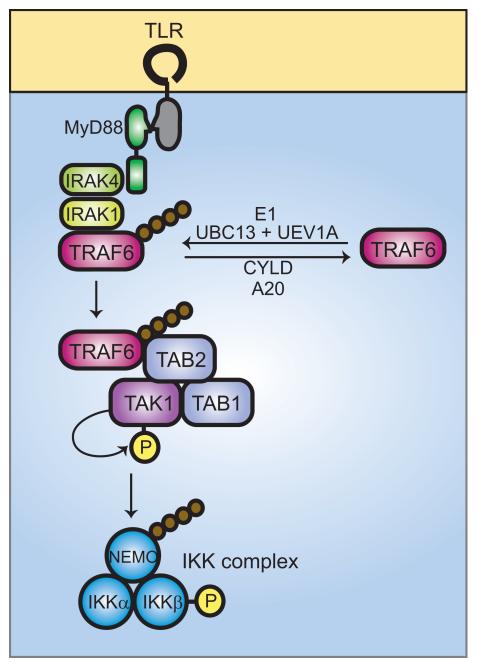
Fig. 2. Ubiquitin signaling in TLR-mediated activation of NF-κB.
Ligand binding to TLRs leads to the recruitment of MyD88 and, subsequently, IRAK4 and IRAK1. IRAK1 binds to TRAF6. The oligomerization of TRAF6 (not shown) activates its ubiquitin ligase activity, leading to K63-linked polyubiquitination of NEMO and TRAF6 in conjunction with UBC13 and UEV1A. De-ubiquitination can be carried out by CYLD and A20. Ubiquitinated TRAF6 recruits the TRIKA2 complex, consisting of TAB1, TAB2, and TAK1, via binding to the novel zinc finger domain of TAB2. TAK1 kinase becomes activated by autophosphorylation and phosphorylates IKKβ at two activation loop serine residues, resulting in IKK complex activation. The IKK complex then phosphorylates IκB, leading to IκB degradation, and releasing NF-κB for translocation to the nucleus.