Figure 2.
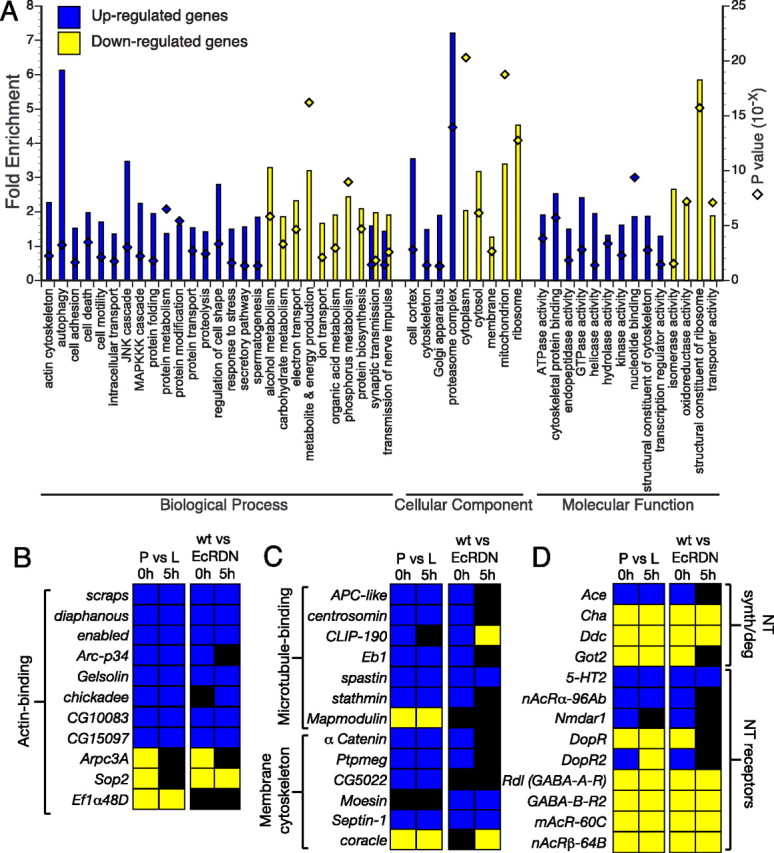
Functional characterization of differentially expressed genes. A, Analysis of Gene Ontology categories for genes that show EcR-dependent upregulation or downregulation at 0 and/or 5 h APF (composite of genes from the orange and purple regions of the Venn diagrams in Fig. 1 D). The graph represents GO categories that are significantly overrepresented (p < 0.05) in the two populations of differentially expressed genes. The bars indicate the fold enrichment (left y-axis) of the genes belonging to a particular GO term in the population of regulated genes, compared with the total population of genes on the DrosGenome1 array. The diamonds indicate the modified Fisher's exact p value (EASE score; right y-axis) for each category. Genes were classified by using a set of 179 GO categories for biological processes, cellular components, and molecular function (GO essential slim) (Tomancak et al., 2007). A given gene may belong to more than one group; for details, see supplemental Tables S3 and S4 (available at www.jneurosci.org as supplemental material). B, C, Genes encoding actin-binding (B) and microtubule-binding proteins or proteins associated with the membrane cytoskeleton (C) are differentially regulated by EcR in MB neurons. Gene functions are inferred from GO terms in Flybase and the study by Goldstein and Gunawardena (2000). Color convention for fold expression change is the same as in Figure 1 E. D, Regulation of genes encoding NT receptors and proteins involved in NT synthesis and degradation. Gene function is inferred from GO terms in Flybase.
