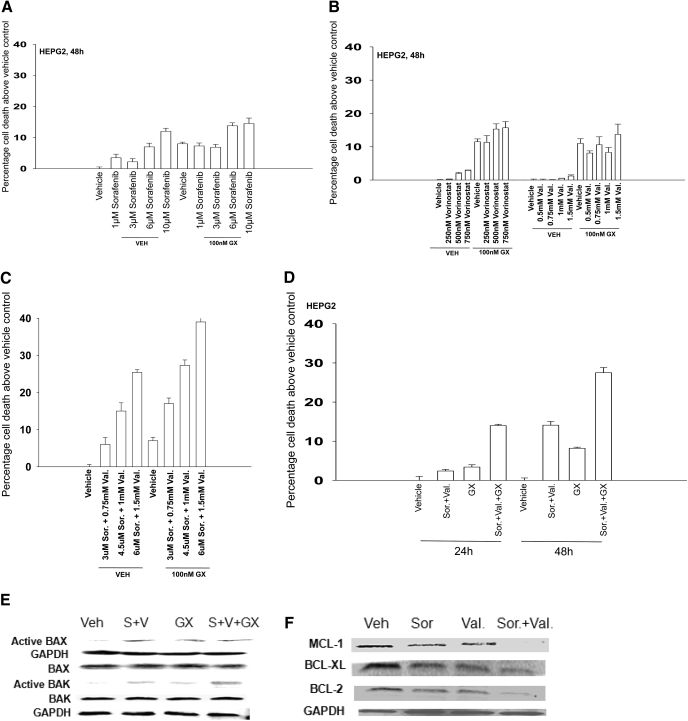
Fig. 4.
Sorafenib and sodium valproate combination lethality is enhanced by GX15-070 (obatoclax). A, HEPG2 cells were treated with vehicle or GX15-070 in the presence or absence of sorafenib. Cells were isolated after 48 h, and viability was determined using trypan blue exclusion (± S.E.M., n = 3). B, HEPG2 cells were treated with vehicle or GX15-070 in the presence or absence of either vorinostat or sodium valproate. Cells were isolated after 48 h, and viability was determined using trypan blue exclusion (± S.E.M., n = 3). C, HEPG2 cells were treated with vehicle or GX15-070 in the presence or absence of sodium valproate and sorafenib. Cells were isolated 48 h after exposure, and viability was determined using trypan blue exclusion (± S.E.M., n = 3). D, HEPG2 cells were treated with vehicle or GX15-070 in the presence or absence of sorafenib and sodium valproate. Cells were isolated 24 and 48 h after drug exposure, and viability was determined using trypan blue exclusion (± S.E.M., n = 3). E, HEPG2 cells were treated with vehicle or GX15-070 in the presence or absence of sodium valproate and sorafenib. Twenty-four hours after treatment, the activation of BAX and BAK was determined after immunoprecipitation (n = 3). F, HEPG2 cells were treated with vehicle in the presence or absence of sodium valproate and/or sorafenib. Twenty-four hours after treatment, the expression of BCL-2, BCL-XL, and MCL-1 was determined by SDS-PAGE/blotting (n = 3).