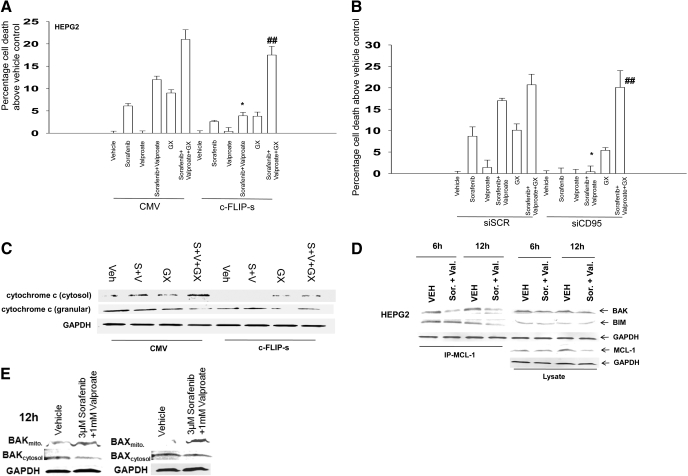
Fig. 5.
The BCL-2/BCL-XL/MCL-1 inhibitor GX15-070 promotes sorafenib and valproate-induced killing and circumvents the protective effects of either CD95 knockdown or c-FLIP-s over-expression. A, HEPG2 cells were infected with recombinant adenoviruses, and 24 h after infection, cells were treated with vehicle, sodium valproate, sorafenib, or sorafenib + valproate, and in parallel with either vehicle or GX15-070. Twenty four hours after exposure, cell viability was determined using trypan blue exclusion assays (± S.E.M., n = 3). *, p < 0.05 less than corresponding value in CMV vector cells; ## p < 0.05 greater than cells lacking GX15-070. B, HEPG2 cells were transfected with siRNA to knockdown CD95 (siCD95). Cells were treated 36 h later with vehicle, sodium valproate, sorafenib, or sorafenib + vorinostat and in parallel with either vehicle or GX15-070. Twenty-four hours after drug exposure, viability was determined using trypan blue exclusion (± S.E.M., n = 3). *, p < 0.05 less than corresponding value in CMV vector cells; ##, p < 0.05 greater than cells lacking GX15-070. C, sets of HEPG2 cells parallel to those in A were treated with drugs, and 24 h after exposure, cell fractionation to isolate the crude granular and cytosolic fractions was performed to determine cytochrome c levels (n = 2). D, HEPG2 cells were treated with vehicle, sodium valproate, sorafenib, or sorafenib + vorinostat, and 12 hours after exposure, equal portions of cell lysate were subjected to immunoprecipitation for MCL-1 or for immunoblotting for total levels of BAK, BIM, and MCL-1 (n = 2). E, HEPG2 cells were treated with vehicle, sodium valproate, sorafenib, or sorafenib + vorinostat, and 12 h after exposure, cytosolic and crude granular fractions obtained by differential centrifugation. Equal protein-equal portions of the lysate was subjected to SDS-PAGE followed by immunoblotting to determine the total levels of BAK and BAX in each cell fraction (n = 2).