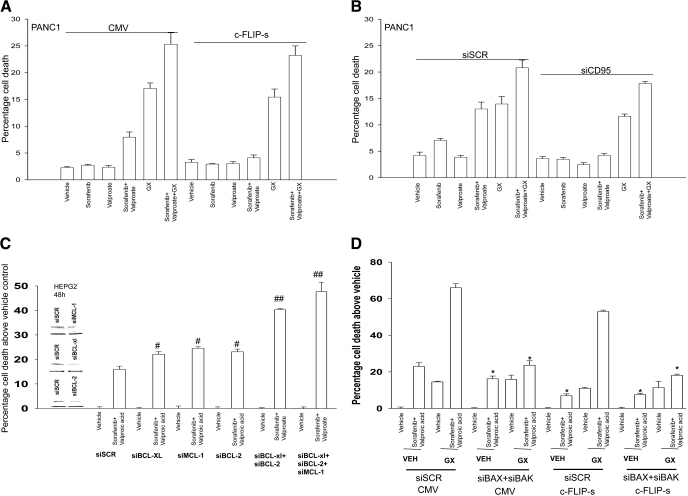
Fig. 6.
GX15-070 promotes sorafenib + valproate-induced killing in pancreatic cancer cells. A, PANC1 cells were infected with recombinant adenoviruses, and twenty-four hours after infection, cells were treated with vehicle, sodium valproate, sorafenib, or sorafenib + valproate, in parallel with either vehicle or GX15-070. Twenty-four hours after exposure, cell viability was determined using trypan blue exclusion assays. B, PANC1 cells were transfected with siRNA to knockdown CD95 (siCD95). Thirty-six hours after transfection, cells were treated with vehicle, sodium valproate, sorafenib, or sorafenib + vorinostat and in parallel with either vehicle or GX15-070. Twenty-four hours after exposure, cell viability was determined using a trypan blue exclusion assay (± S.E.M., n = 3). C, HEPG2 cells were transfected with scrambled siRNA or transfected with siRNA molecules to knockdown BCL-2, BCL-XL, MCL-1, BCL-2 + BCL-XL, or BCL-2 + BCL-XL + MCL-1 expression. Thirty-six hours after transfection, cells were treated with vehicle, valproate, and sorafenib. Forty-eight hours after exposure, cell viability was determined using a trypan blue exclusion assay(± S.E.M., n = 4). #, p < 0.05 greater than corresponding value in siSCR cells; ##, p < 0.05 greater than cells with single knockdown of a BCL-2 family protein. D, HEPG2 cells were transfected with scrambled siRNA or transfected with siRNA molecules to knockdown BAX and BAK. In parallel, the cells were infected with empty vector virus (CMV) or a virus to express c-FLIP-s. Thirty-six hours after transfection, cells were treated with vehicle, valproate + sorafenib, GX15-070, or GX15-070 + valproate + sorafenib. Forty-eight hours after exposure, cell viability was determined using a trypan blue exclusion assay (± S.E.M., n = 2). *, p < 0.05 less than corresponding value in siSCR cells.