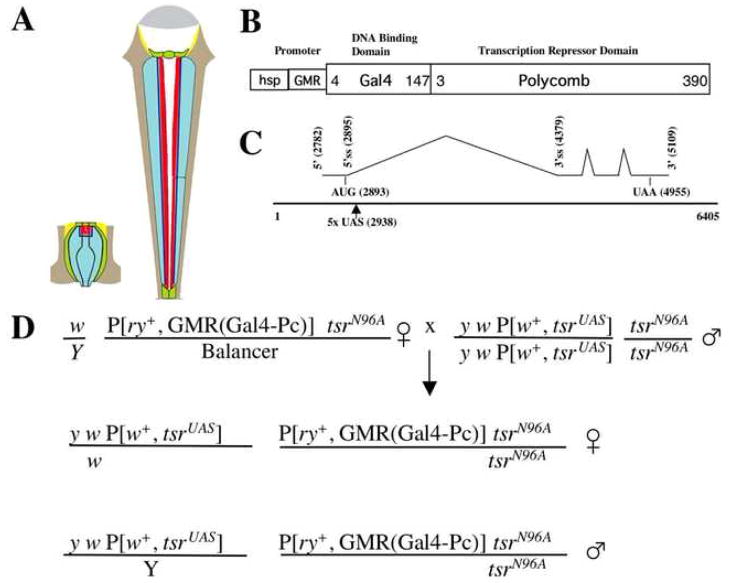
Figure 1.
(A) The diagram shows the structure of a mid-pupal (left) and adult (right) ommatidium. The adult ommatidium is longer, the result of a 5-fold elongation during pupal development. As the photoreceptor cells elongate, the rhabdomeres (red) and adherens junctions (dark blue) elongate with the cells. This drawing was modified from (Tepass and Harris, 2007). (B) P[ry+; GMR(Gal4-Pc)] contains the eye specific GMR promoter (Ellis et al., 1993; Moses and Rubin, 1991) driving expression of the Gal4-Pc hybrid protein, which encodes the DNA binding domain of Gal4 (amino acids 4-147) and the repressor domain of Polycomb (amino acids 3-390). The construct also contains the heat shock inducible hsp70 promoter adjacent to the GMR promoter. (C) P[w+; tsrUAS] contains the tsr 6.4 kb genomic rescue fragment, into which was inserted a cassette containing 5 copies of the Gal4 UAS DNA binding site. P[w+; tsrUAS] is capable of completely rescuing a tsr null mutation. Base pair positions within the 6.4 kb rescue construct are shown. (D) Genetic cross used to generate the tsr RS mutant flies. TSTL, the compound CyO, TM6B Tb chromosome was used as a balancer.