Figure 2.
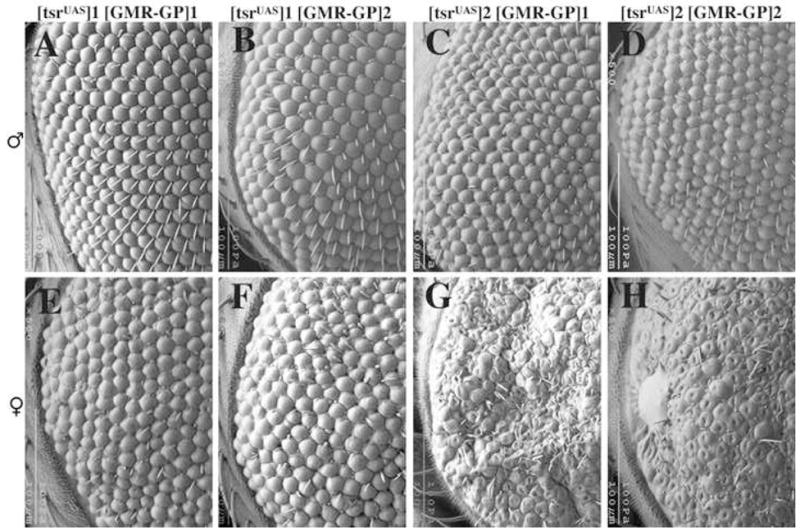
A phenotypic series of tsr RS eye mutants is seen in the scanning electron micrographs of one day-old adults. The flies are homozygous for the tsr null allele tsrΔ96 but are viable and healthy because they contain the P[w+, tsrUAS] genomic rescue construct on the X chromosome. These flies also have a construct which expresses Gal4-Polycomb (GP) from the GMR eye specific promoter. Gal4-Pc will bind to the UAS sites in P[w+, tsrUAS] and inhibit expression of tsrUAS. Two different P[w+, tsrUAS] inserts on the X chromosome (insert 1 and 2) and two different P[ry+; GMR(Gal4-Pc)] inserts on the second chromosome (inserts 1 and 2) were analyzed and found to have position effect differences. Females were found to have a more severe phenotype than males of the same genotype, likely the result of dosage compensation of P[w+, tsrUAS] on the X chromosome. The genotypes are: (A) y w P[w+, tsrUAS]1/Y, P[ry+; GMR(Gal4-Pc)]1 tsrN96A/tsrN96A (B) y w P[w+, tsrUAS]1/Y, P[ry+; GMR(Gal4-Pc)]2 tsrN96A/tsrN96A (C) y w P[w+, tsrUAS]2/Y, P[ry+; GMR(Gal4-Pc)]1 tsrN96A/tsrN96A (D) y w P[w+, tsrUAS]2/Y, P[ry+; GMR(Gal4-Pc)]2 tsrN96A/tsrN96A (E) y w P[w+, tsrUAS]1/w, P[ry+; GMR(Gal4-Pc)]1 tsrN96A/tsrN96A (F) y w P[w+, tsrUAS]1/w, P[ry+; GMR(Gal4-Pc)]2 tsrN96A/tsrN96A (G) y w P[w+, tsrUAS]2/w, P[ry+; GMR(Gal4-Pc)]1 tsrN96A/tsrN96A (H) y w P[w+, tsrUAS]2/w, P[ry+; GMR(Gal4-Pc)]2 tsrN96A/tsrN96A.
