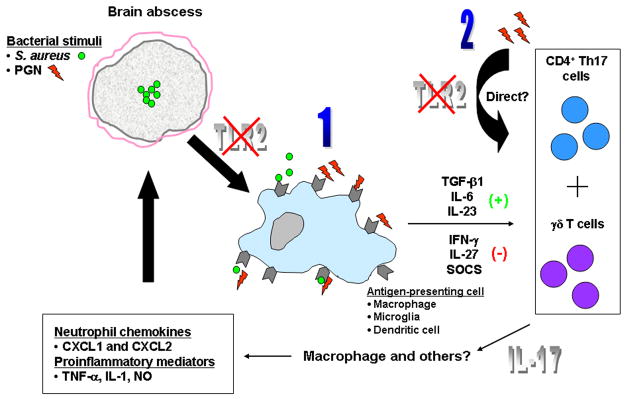
Figure 13. Potential mechanisms of exaggerated IL-17 expression in brain abscesses of TLR2 KO mice.
The absence of TLR2 signaling could lead to elevated IL-17 expression in a number of potential ways including (1) changes in APC properties or (2) direct effects on T cell populations. Based on the pro-inflammatory effects of IL-17, we propose that this response compensates for the loss of TLR2 signaling to result in an effective host anti-bacterial immune response.