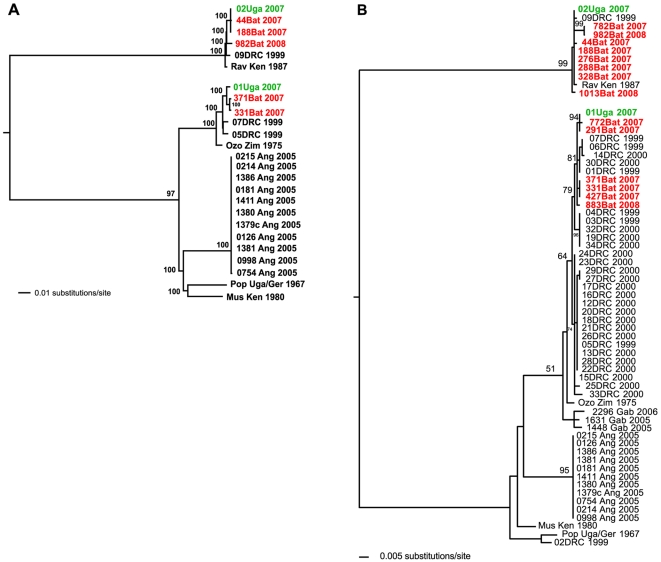
Figure 2. Phylogenetic analysis of full-length or partial genomes of Marburg viruses isolated from humans or bats (see Table S1 for Genbank accession numbers).
Trees shown are maximum-likelihood analyses with Bayesian posterior probabilities >50 listed at the appropriate nodes. The ebolavirus outgroup used during the Bayesian phylogenetic analyses are denoted by the small twig at the root of the tree. Marburg virus sequences from 2007 human cases in Uganda are in green, while those from bats are listed in red. (A) Analysis of full-length genomes of five Marburg virus bat isolates, 18 historical isolates, and the isolates from patients A and B (01Uga07 and 02Uga07 respectively). (B) Phylogenetic analysis of concatenated NP and VP35 sequence fragments obtained from each bat specimen compared to corresponding regions from 48 historical isolates and those from 01Uga07 and 02Uga07.