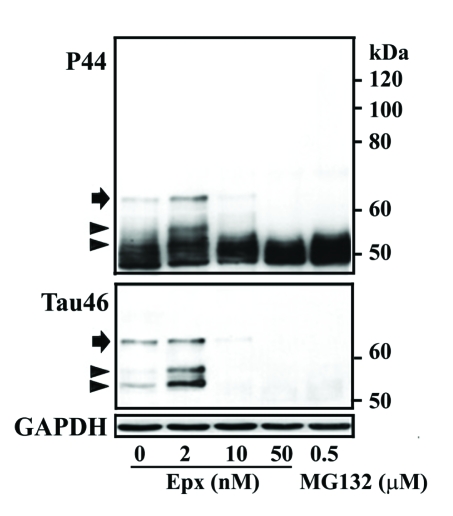
Figure 2.
Dose-dependent impacts of proteasome inhibition on tau processing. M1C cells were subjected to a 5-day TetOff induction plus exposure to epoxomicin (Epx) at 2 or 10 nM for 2 days or at 50 nM for 1 day or to 0.5 μM MG132 for a day before such induction ended. Cultures treated with DMSO served as vehicle control (Epx 0). Cell lysates were immunoblotted with antibody P44 (top panel) and reprobed with antibody Tau46 (mid-panel). Replica blot was probed with GAPDH antibody to verify loading (bottom panel). In the 2 nM Epx-treated, tau species of 62, 54 and 52 kDa displayed P44, Tau46 and E1 (data not shown) immunoreactivities, suggesting that they are intact tau with different extents of posttranslational modification. Based on Tau46 immunoblotting, the 52-kDa (arrowhead) was the most abundant followed by 54 (arrowhead) and 62 kDa (arrow). In contrast, in vehicle-treated cells, the 62-kDa was the most abundant followed by 52 and 54 kDa species. In cultures exposed to Epx at higher concentrations or to MG132 Tau46-positive tau species were reduced or not detectable, but P44-positve tau species were observed, indicating most of these tau are carboxyl-terminally truncated.