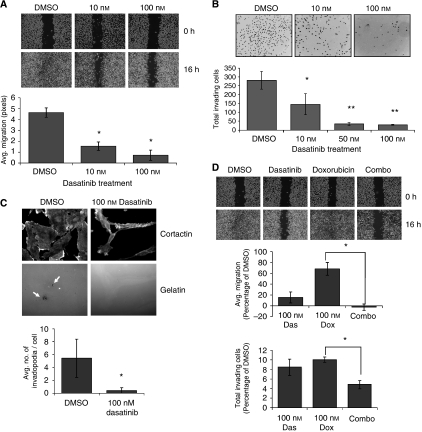
Figure 5.
Doxorubicin and dasatinib synergize to block migration and invasion of MDA-MB-231 cells. (A) MDA-MB-231 cells were grown to 80% confluence in glass chamber slides and treated for 6 h before being streaked with a sterile pipette tip. Phase contrast images were taken at 0 and 6 h after wounding. All bright field images were obtained at × 10 magnification and wound width quantified (in pixels) using the NIH Image J software. (B) Cells were pre-treated with dasatinib for 4 h before transfer to Matrigel invasion chambers in serum-free, dasatinib-containing media. Cells were allowed to invade for 16 h towards media containing 10% FCS plus dasatinib. Data represent the average number of invading cells per membrane. (C) MDA-MB-231 cells were plated on FITC-gelatin in media containing DMSO or 100 nM dasatinib and allowed to adhere and invade for 20 h. Cells were then stained for cortactin, and invadopodia counted as co-localisations of cortactin staining and degraded FITC-signal (indicated by white arrows) in 10 random fields per sample. Results represent the average number of invadopodia per cell. (D) Wound healing and Matrigel invasion assays were repeated as in panels A and B, with dasatinib-, doxorubicin-, or combination (100 nM each drug)-treated cells. Error bars represent s.d. *Indicates P<0.05; **indicates P<0.01.