Fig. 1.
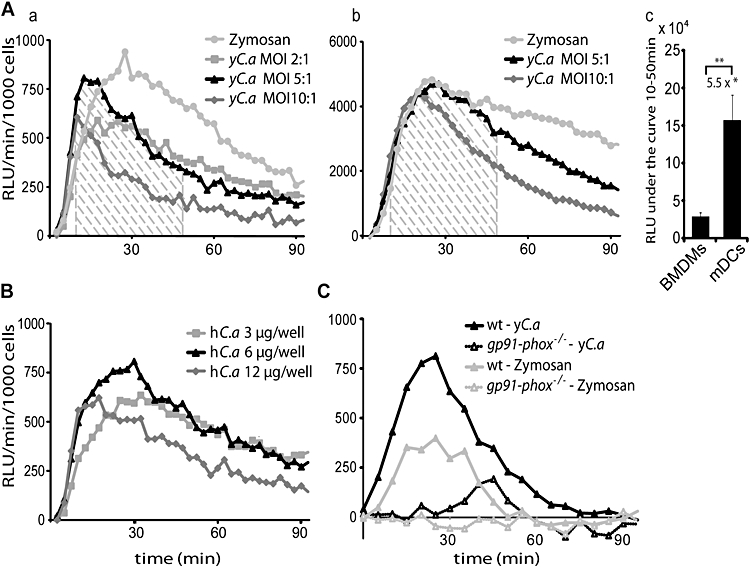
C. albicans induces ROS production in wild-type BMDMs and mDCs. A–C. ROS measurement by luminol-dependent chemiluminescence at 37°C in 2.5 min intervals over a 90 min period [relative luciferase units (RLU) min−1 per 1000 immune cells]. A. Stimulation of BMDMs (a) or mDCs (b) with yeast-form C. albicans (yC.a) at an MOI of 2:1 (equivalent to 2 μg yeast dry weight per well), 5:1 (5 μg/well) or 10:1 (10 μg/well) or with zymosan (20 μg/well). (c) Quantification of the total ROS release between 10 and 50 min (striped area) by calculating the area under the curve (MOI 5:1). The average of three independent experiments is presented. *mDCs produce 5.5 ± 0.35 times more ROS than BMDMs. **P < 0.02. B. Stimulation of BMDMs with hyphae-form C. albicans (hC.a) at 3 μg dry weight/well, 6 μg/well or 12 μg/well. C. Stimulation of gp91phox−/− and wt BMDMs with yeast-form C. albicans at an MOI of 5:1 or zymosan (20 μg/well). A–C. Results of one experiment per condition are shown. Data were reproduced in at least three independent experiments. Statistical significance was calculated using a two-tailed Student's t-test.
