Fig. 5.
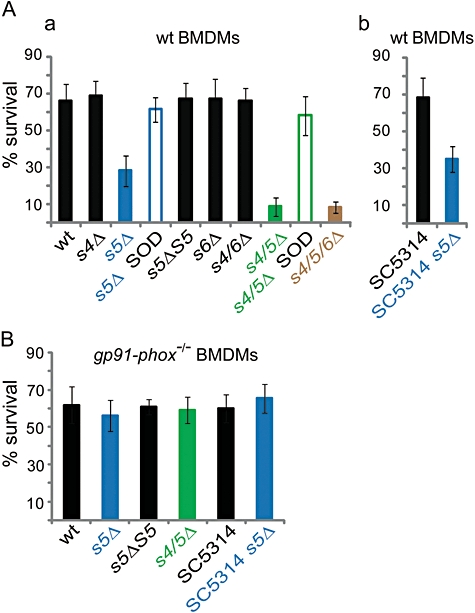
sod5Δ/Δ and sod4Δ/Δsod5Δ/Δ strains are hypersensitive to killing by BMDMs. A and B. Survival of C. albicans and isogenic mutant cells was determined using the end-point dilution assay. Mean and standard deviation of three independent experiments are presented. A. Wild-type BMDMs in medium without (filled bars) or with 10 U commercial erythrocyte SOD (white bar) were coincubated with either wild-type (wt) C. albicans strain or strains lacking SOD4 (s4Δ), SOD5 (s5Δ blue), the restored SOD5 (s5ΔS5), SOD6 (s6Δ) or strains lacking both SOD4 and SOD6 (s4/6Δ), SOD4 and SOD5 (s4/5Δ green) or lacking all three SOD4, SOD5 and SOD6 (s4/5/6 brown) (a), or with the clinical isolate SC5314 and the sod5Δ/Δ mutant in the SC5314 background (SC5314 s5Δ blue) (b) for 48 h at 37°C with 5% CO2. B. gp91phox−/− BMDMs were infected with the wild type (wt) or strains lacking SOD4 (s4Δ), SOD5 (s5Δ blue), the restored SOD5 (s5ΔS5) or strains lacking both SOD4 and SOD5 (s4/5Δ green), the clinical isolate SC5314 or the sod5Δ/Δ mutant in the SC5314 background (SC5314 s5Δ). The percentage of survival for each strain was determined as follows (colonies in absence of BMDMs versus colonies in presence of BMDMs × 100).
