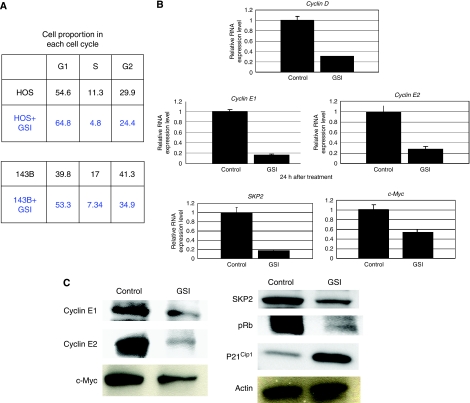
Figure 4.
Notch pathway inhibition promotes G1 arrest. HOS and143B cells were treated with 5 μM GSI. After 48-h treatment, cells were collected and subjected to cell cycle analysis. When HOS cells were cultured without GSI, 54.6% of cells were in G1 phase. On the other hand, when cultured with GSI, 64.8% of cells were in G1 phase. In the case of 143B cells cultured without GSI, 39.8% of cells were in G1 phase, whereas 53.3% of cells were in G1 phase when treated with GSI (A). Real-time PCR was carried out to quantify mRNAs of cell cycle-related genes. A 24-h treatment with GSI reduced the levels of cyclin D, cyclin E1, E2, SKP2, and c-Myc transcription (error bar means s.d.; B). Western blot analysis of the levels of cell cycle-related genes. 48 h treatment with GSI reduced the levels of expression of cyclin E1, cyclin E2, c-Myc, pRb, and SKP2 proteins. Expression of P21cip1 protein was upregulated by GSI treatment. The experiment was triplicate with similar results (C; GSI: 5 μM).