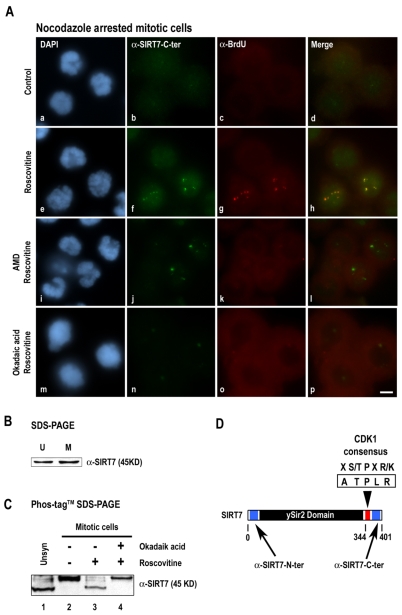
Fig. 5.
Inhibition of CDK1-cyclin B induces increased reactivity of antibodies to the SIRT7 C-terminal region by SIRT7 dephosphorylation. (A) SIRT7 and rDNA transcription sites were immunodetected using anti-SIRT7-C-terminal (b,f,j,n) and anti-BrdU (c,g,k,o) antibodies in prometaphase mitotic HeLa cells, in the absence (a-d) or presence (e-h) of roscovitine (150 μM for 1 hour). Mitotic HeLa cells were also treated with AMD (0.1 μg/ml, i-l) or okadaic acid (0.5 μM, m-p) for 1 hour before addition of 150 μM roscovitine for 1 hour. Red and green labelings were merged (d,h,l,p). (B) Whole cell extracts from unsynchronized (U) or nocodazole-arrested mitotic (M) HeLa cells were submitted to 10% SDS-PAGE. Immunodetection of SIRT7 was performed using anti-SIRT7-N-terminal antibodies. (C) Whole cell extracts prepared from unsynchronized HeLa cells (Unsyn, lane 1) and from nocodazole-arrested mitotic HeLa cells (lanes 2-4) treated with okadaic acid (0.5 μM for 1 hour) (lane 4) or not (lane 3) before addition of roscovitine (150 μM for 1 hour) (lanes 3 and 4) were submitted to 7.5% Phos-tag SDS-PAGE. Immunodetection of SIRT7 was performed using anti-SIRT7-N-terminal antibodies. (D) SIRT7 presents a consensus CDK1 phosphorylation site (ATPLR) at amino acids 344-348 (red box). Blue boxes indicate the peptides against which anti-SIRT7-N-terminal antibodies (amino acids 32-51) and anti-SIRT7-C-terminal antibodies (amino acids 384–400) are directed. Bar, 10 μm.