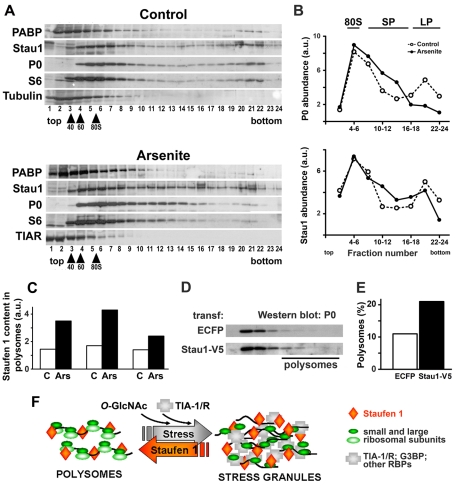
Fig. 6.
Stau1 associates with stress-resistant polysomes. (A) NIH 3T3 cells were exposed to 0.5 mM arsenite for 1 hour, polysomes were separated in sedimentation gradients and fractions were analyzed by western blot to detect P0, a marker for large ribosomal subunits, S6, a marker for small subunits, PABP, TIAR and Stau1. (B) Distribution of P0 and Stau1 in pooled fractions from the gradient shown in A were evaluated by western blot and relative abundances are represented in the graphs. (C) Three independent experiments were performed as in A, and the distribution of polysomes was evaluated by following the P0 and S6 distributions in the gradient. Left column pair, total number of fractions = 13; polysome-containing fractions = 10-13. Middle and right column pairs, total number of fractions = 24; polysome-containing fractions = 16-24. The content of Stau1 in the polysomal fraction was measured by western blot analysis and is expressed normalized to S6 (left column pair) or P0 (middle and right column pairs). Duplicate western blot analysis of each gradient showed variations less than 10%. On average, the polysomes that remain upon stress induction contain twice the amount of Stau1 than found in polysomes under resting conditions. (D,E) Cells were transfected with ECFP or Stau1-V5 and exposed to 0.5 mM arsenite for 1 hour. The polysome profile was evaluated by monitoring the distribution of P0 in the gradient and the relative amount of polysomes is expressed as the percentage of P0 in the polysomal fraction relative to total. The amount of polysomes recovered after stress induction was increased from 10 to 20% in the presence of Staufen1-V5. (F) A model for the modulation of stress granules by Stau1. Under resting conditions, Stau1 is associated with polysomes by binding to mRNAs and ribosomal subunits. Cellular stress or pharmacological inhibition of 60S ribosomal recruitment provokes the breakdown of polysomes and concomitant accumulation of abortive translation initiation complexes that are aggregated by specific RBPs including TIA-1, TIAR and G3BP and by the O-glycosylation of ribosomal proteins (reviewed by Anderson and Kedersha, 2008; Ohn et al., 2008). Stau1 is recruited to growing stress granules by a piggyback mechanism. Formation of stress granules is counterbalanced by Stau1, which stabilizes polysomes against stress-induced breakdown, thus helping stress granule dissolution. In addition, Hsp70 contributes to stress granule disassembly (Mazroui et al., 2007).