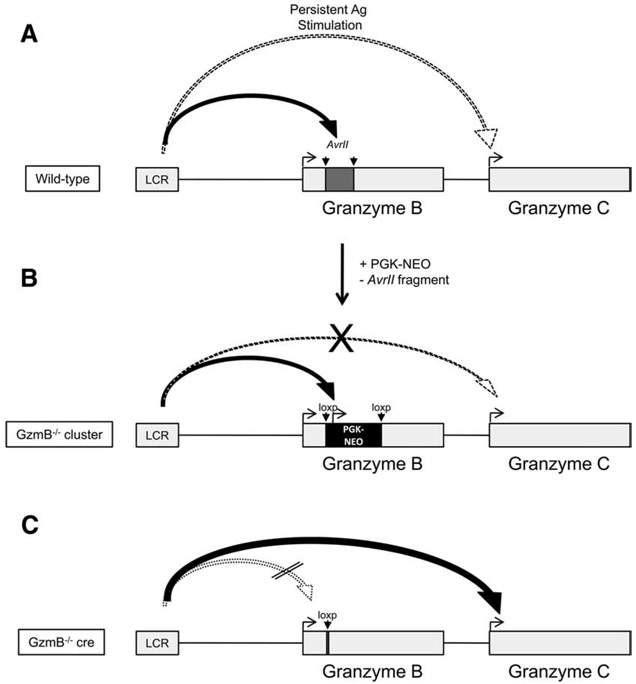
FIGURE 10.
Model of granzyme B and C regulation in WT, GzmB−/− cre, and GzmB−/− cluster-derived cytotoxic lymphocytes. In WT cytotoxic lymphocytes (A), the LCR first interacts with regulatory elements within or near the AvrII fragment of granzyme B to induce transcription. Granzyme C is induced only after prolonged activation. GzmB−/− cluster-derived cytotoxic lymphocytes (B) have the normal AvrII fragment replaced with a PGK-neo cassette and fail to express granzyme B due to disruption of the gene. In addition, granzyme C expression is diminished due to the neighborhood effect created by the retained PGK-neo cassette. In GzmB−/− cre CTLs (C), granzyme C is expressed earlier and more abundantly (similarly to granzyme B in WT cells), because missing regulatory elements in granzyme B cause the LCR to “scan” downstream and activate the next gene in the cluster. Removal of the PGK-neo cassette eliminates the neighborhood effect.