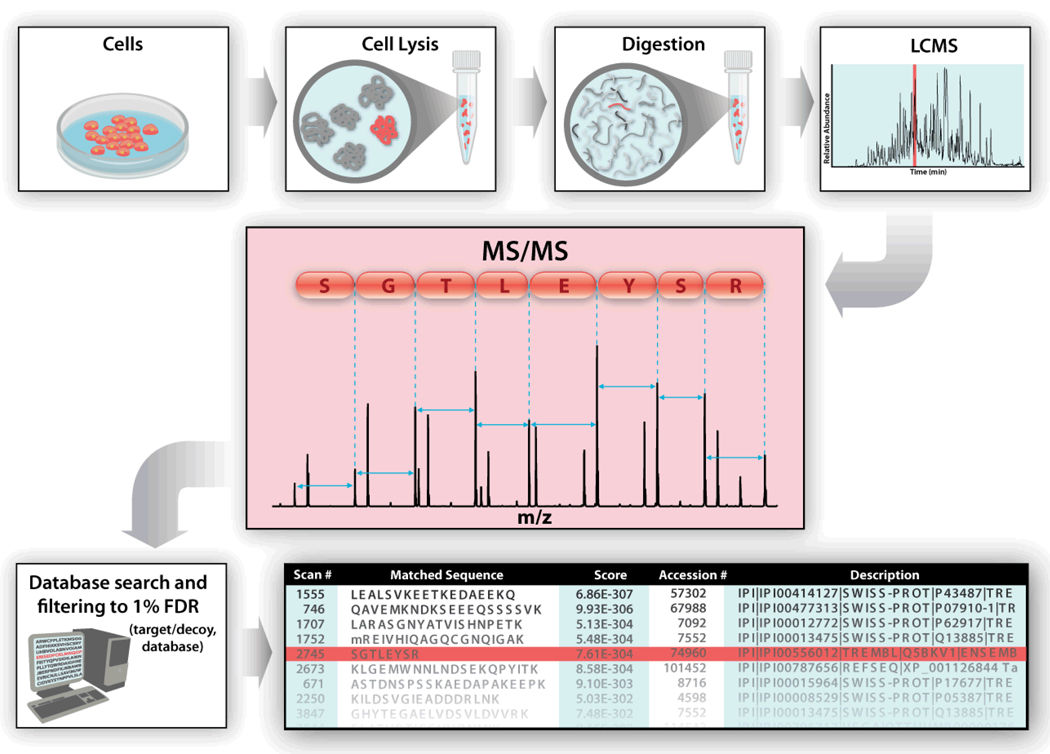
Figure 1.
Overview of contemporary proteomics methodology. Extracted proteins are enzymatically digested to produce highly complex mixtures of peptides that are then sorted with one or multiple dimensions of chromatography. The final stage of chromatography is generally coupled to a mass spectrometer through an electrospray interface. Peptide precursor cations are selected for analysis by MS/MS to produce spectra like the one shown in the red box. The thousands of these spectra collected per hour are then exported to database correlation algorithms where spectra having good matches to peptides present in a database are displayed to the user. The success of this approach, however, relies heavily upon the MS/MS step producing a sufficient number of fragment ions for spectral matching.