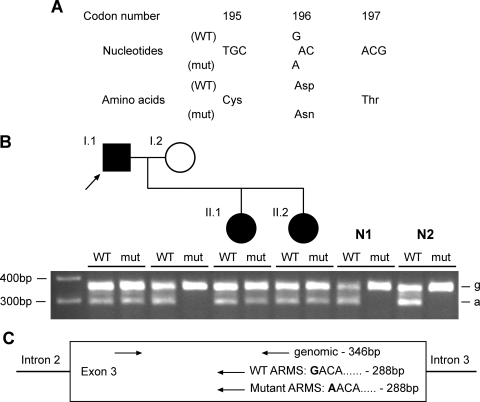
Figure 2.
Detection and confirmation of novel Uromodulin mutation D196N in family 04/03 (Table 1). (A) DNA sequence analysis of individual I.1 revealed a heterozygous G-to-A transition at codon 196, thus altering the wild-type (WT) sequence GAC, encoding an aspartate (D), to the mutant (mut) sequence AAC, encoding an asparagine (N). (B) The D196N mutation was confirmed in the proband (arrowed) by ARMS-PCR, which also showed that the mutation was present in the other affected family members (II.1, II.2), but absent in a panel of 55 normal individuals, of which two (N1, N2) are shown. For each individual, ARMS-PCR products are loaded wild-type (WT)—mutant (mut). ‘g’ denotes genomic band, ‘a’ denotes ARMS band, as shown in the schematic diagram (C). Each ARMS primer was used in a reaction with both genomic primers.