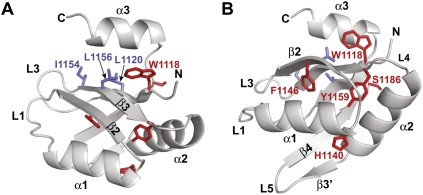
FIGURE 4.
Ribbon representation of the D. melanogaster GW182 RRM showing the β-sheet surface normally involved in RNA binding (A) or the opposite helical surface (helix α1 and helix α2) (B). The C-terminal α-helix α3 covers the β-sheet surface, which in canonical RRMs is involved in RNA binding (Eulalio et al. 2009b). Side chains of aliphatic residues, which are normally aromatic in RNP1 and RNP2 motifs of canonical RRMs are shown as blue sticks. Residues corresponding to those mutated by Zipprich et al. (2009) in TNRC6C are shown as red sticks. Residues F1146 (F1543 in TNRC6C) and Y1159 (Y1556 in TNRC6C) are part of the hydrophobic core of the domain, whereas W1118 (W1515 in TNRC6C) contributes to hydrophobic interactions with α-helix α3.