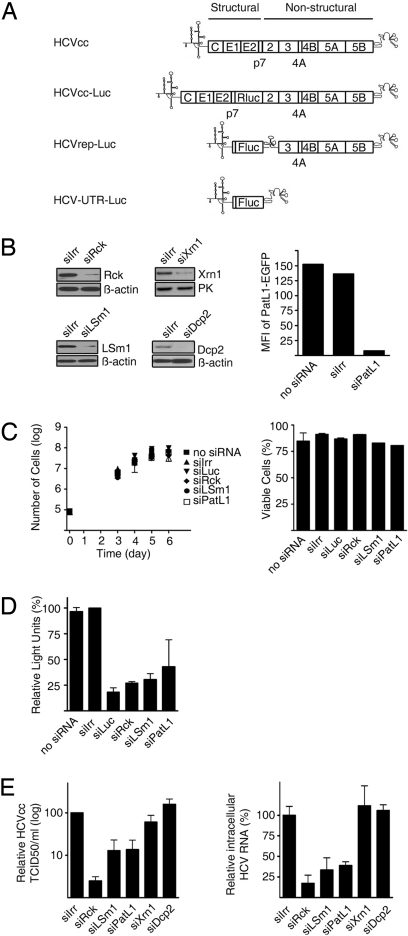
Fig. 1.
Depletion of Rck/p54, LSm1 or PatL1 in hepatoma cell lines impairs HCV replication. (A) Schematic representations of the genomes of HCVcc, HCV Replicons and derivatives used in this study. (B) Huh7-Lunet cells were transfected with siRNA targeting Rck/p54, LSm1, PatL1, Xrn1, Dcp2, or a nontargeting siRNA (siIrr). Immunoblot analyses of Rck/p54, LSm1, Xrn1, Dcp2, β-actin, or pyruvate kinase levels are shown. Because no specific antibody is available for PatL1, to test PatL1 silencing, PatL1-EGFP expression plasmid and siRNAs were cotransfected and fluorescence was analyzed 1 day later by flow cytometry. Values are expressed in mean fluorescence intensity (MFI) (bar graph). Similar silencing results were obtained for Huh7.5 cells. (C) Cell growth of siRNA-transfected cells was followed for 6 days by counting the total number of cells (mean ± SEM; n = 3) (Left). The percentage of viable silenced cells at the day of maximum silencing was measured by propidium iodide staining (mean ± SEM; n = 2) (Right). (D) Huh7-Lunet cells were coelectroporated with the HCVrep-Luc replicon and the siRNAs. The percentage of relative luciferase light units compared with siIrr-transfected cells is shown at the day of most efficient silencing (mean ± SEM; n = 2). (E) Three days after transfection of silenced Huh7.5 cells with HCVcc RNA, the HCVcc infectivity in the supernatant was titrated by a limited dilution assay (Left). The accumulation of intracellular HCVcc mRNA was analyzed by quantitative RT-PCR (Right). Both values were normalized to the amount of transfected RNA (mean ± SEM; n = 3) and are shown relative to siIrr-transfected cells.