Figure 1. Nrf2 was Required for the p21-Dependent Cellular Protection in Response to Oxidative Stress.
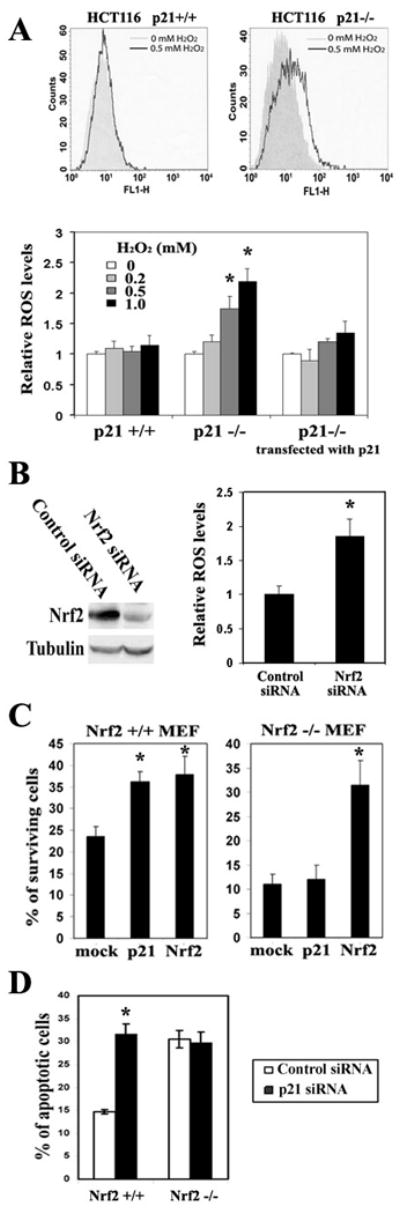
(A) p21 exhibited antioxidant functions. HCT116-p21+/+, HCT116-p21-/-, and HCT116-p21-/- cells transfected with an expression vector for p21, were treated with the indicated doses of H2O2 for 12 hrs. Intracellular ROS levels were measured by the dichlorofluorescein/flow cytometry method. The representative histograms of ROS analysis in HCT116-p21+/+cells and HCT116-p21-/- cells are shown in the upper two panels. (B) HCT116-p21+/+ cells with knockdown of Nrf2 had higher intracellular levels of ROS. HCT116-p21+/+ cells were transfected with either control siRNA or Nrf2-siRNA. At 72 hrs post-transfection, levels of Nrf2 and intracellular ROS were measured. (C) Ectopic expression of p21 enhanced cell survival in response to H2O2 in MEF-Nrf2+/+, but not in MEF-Nrf2-/- cells. MEF-Nrf2+/+ or MEF-Nrf2-/- cells were cotransfected with the indicated expression vectors for 24 hrs. GFP was used to mark the transfected cells. Following treatment with H2O2, over 150 GFP positive cells were counted for both surviving and apoptotic cells by fluorescence microscopy. The percentage of surviving cells was plotted. (D) Knockdown of p21 sensitized cells to H2O2-induced cell death in MEF-Nrf2+/+, but not in MEF-Nrf2-/- cells. Cells were transfected with p21-siRNA or control siRNA for 72 hrs before treatment with H2O2. Apoptotic cells were detected using the Annexin V-FITC/flow cytometry method. All error bars indicate standard deviations calculated from three independent experiments. *p<0.05 compared with its control.
