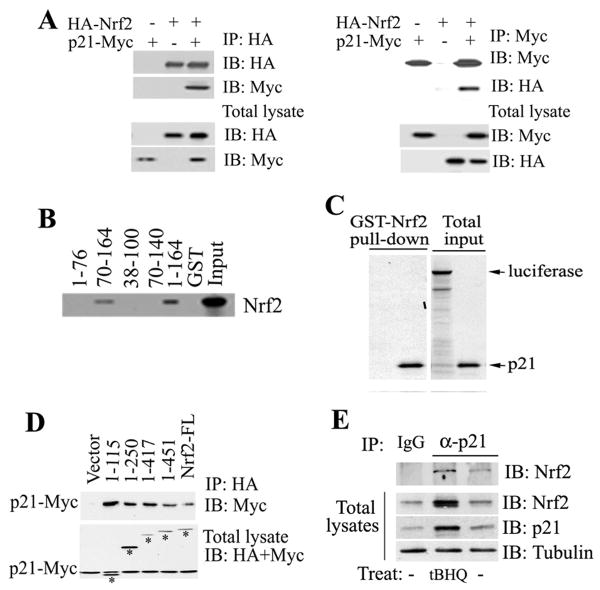
Figure 4. p21 Directly Interacted with Nrf2.
(A) p21 interacted with Nrf2. COS-1 cell lysates coexpressing p21-Myc and HA-Nrf2 were immunoprecipitated with anti-HA (left panel) or anti-Myc (right panel) antibodies. The total lysates (lower two panels) and the immunoprecipitates (upper two panels) were subjected to immunoblot analysis with both anti-HA and anti-Myc antibodies for detection of Nrf2 and p21. (B) The C-terminal domain of p21 was required for direct interaction with Nrf2. GST pull-down analysis were performed with GST-p21 fusion proteins containing different regions of p21 and the 35S-labeled Nrf2 protein. (C) p21 directly interacted with Nrf2. The GST-Nrf2 fusion protein was used to pulldown 35S-labeled p21. Luciferase was used as a negative control. (D) The N-terminal domain of Nrf2 interacted with p21. p21 and each of the Nrf2 C-terminal deletion mutants were coexpressed in COS-1 cells. The Nrf2-containing complexes were immunoprecipitated with HA-beads and blotted with anti-HA and anti-Myc antibodies for detection of Nrf2 and p21. Bands labeled with asterisks are Nrf2 and its deletion mutants. (E) Binding of endogenous p21 to Nrf2 was enhanced in response to oxidative stress. Cell lysates from HCT116-p21+/+cells untreated or treated with tBHQ were subjected to immunoprecipitation analysis with an anti-p21 antibody and then blotted with an anti-Nrf2 antibody (upper panel). An aliquot of total lysate was subjected to immunoblot analysis with anti-Nrf2, anti-p21 and anti-tubulin antibodies (lower three panels).