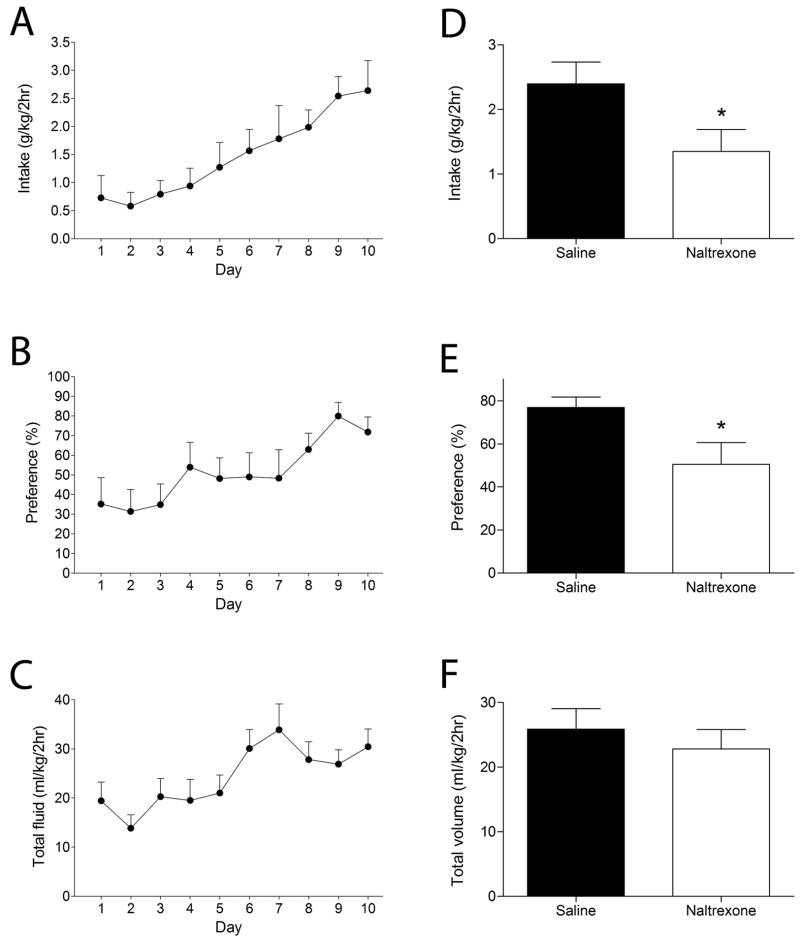
Figure 1. High levels of ethanol consumption under conditions of limited access are naltrexone-sensitive.
Shown are mean ± S.E.M. values from 9 male, wild type mice. Ethanol intake (A), ethanol preference (B) and total fluid intake (C) increased over the 10-day period. Mice were allowed to drink for an additional 4 days. Injection of naltrexone (NTX, 1 mg/kg) i.p. immediately prior to the 2-h session on day 14 reduced ethanol intake (D) and preference (E) without affecting total fluid intake (F). * P < 0.05 compared with vehicle treatment on day 13, by one-tailed, paired t-test.