Figure 1.
Identification of Novel Genes Involved in Met-Derived Glucosinolate Biosynthesis Using Real-Time PCR Analysis and Cotransformation Assays in Cultured Arabidopsis Cells.
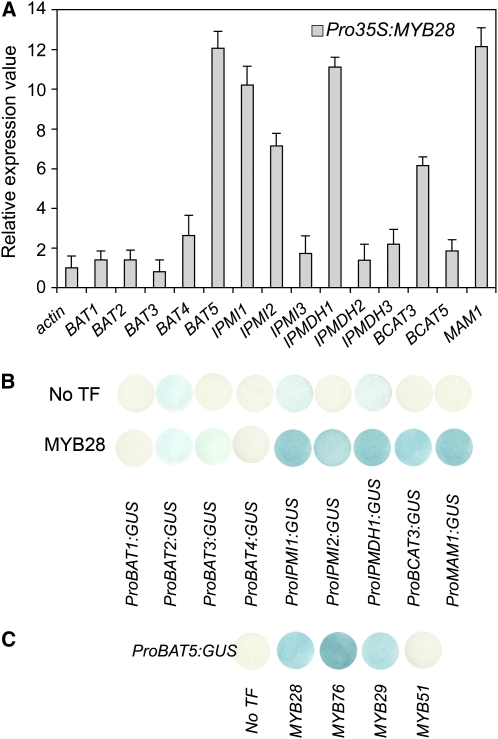
(A) Transcript levels of predicted glucosinolate pathway genes in rosette leaves of 5-week-old HAG1/MYB28 overexpression plants. Relative gene expression values are given compared with the wild type (=1). Means ± sd (n = 3).
(B) Cotransformation assays for the determination of target gene specificity of HAG1/MYB28 (effector) toward target promoters of predicted aliphatic biosynthetic pathway genes are shown. The promoters of BAT1, BAT2, BAT3, BAT4, IPMI1, IPMI2, IPMDH1, and BCAT3 genes were fused to the uidA (GUS) reporter gene (TargetPromoter:GUS vectors). The promoter of the MAM1 gene was used as a positive control. Cultured Arabidopsis cells were inoculated with the supervirulent Agrobacterium strain LBA4404.pBBR1MCS.virGN54D containing either only the reporter construct (TargetPromoter:GUS:pGWB3i) or the reporter construct and the HAG1/MYB28 effector construct (Pro35S:HAG1:pGWB2). GUS staining indicates transactivation of a given promoter by an effector.
(C) Transactivation of ProBAT5:GUS by HAG1/MYB28, HAG2/MYB76, HAG3/MYB29, and HIG1/MYB51.