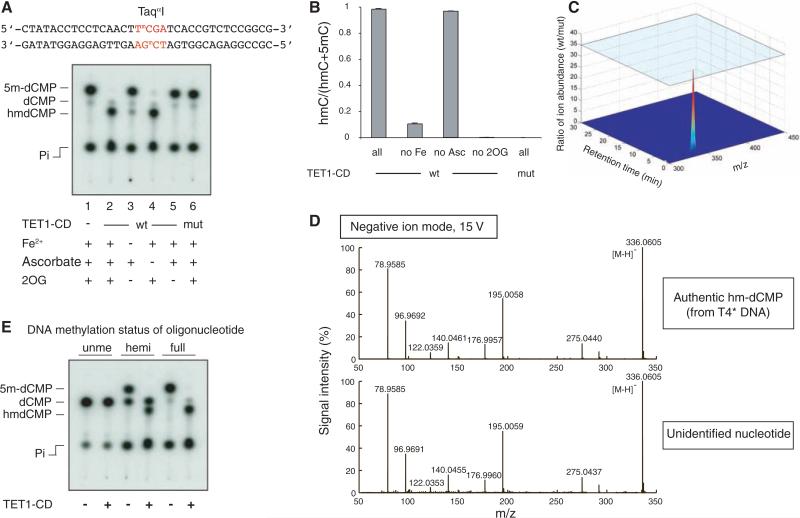
Fig. 4.
Recombinant Flag-HA-TET1-CD purified from Sf9 cells converts 5mC to hmC in methylated DNA oligonucleotides in vitro. (A) Double-stranded DNA oligonucleotides containing a fully methylated TaqαI site were incubated with wt or mut Flag-HA-TET1-CD (1:10 enzyme to substrate ratio). Recovered oligonucleotides were digested with TaqαI and analyzed by TLC. The faint dCMP spot in each lane is derived from end-labeling of the C at the 5′ end of each strand of the substrate. (B) The extent of conversion of 5mC to hmC is shown as the mean ratio [hmC/(hmC+5mC)] ± SD. (C) Comparison of species at an Rf of 0.29 in products resulting from incubation with wt or mut Flag-HA-TET1-CD. (D) MS fragmentation analysis of authentic hm-dCMP (top) and the nucleotide generated by Flag-HA-TET1-CD (bottom). Observed masses are shown in black (mass accuracy was within 0.002 Da). (E) Recombinant Flag-HA-TET1-CD is able to hydroxylate 5mC in fully methylated (full, lanes 5 and 6) and hemimethylated (hemi, lanes 3 and 4) substrates. Unme, unmethylated DNA oligonucleotide (lanes 1 and 2).