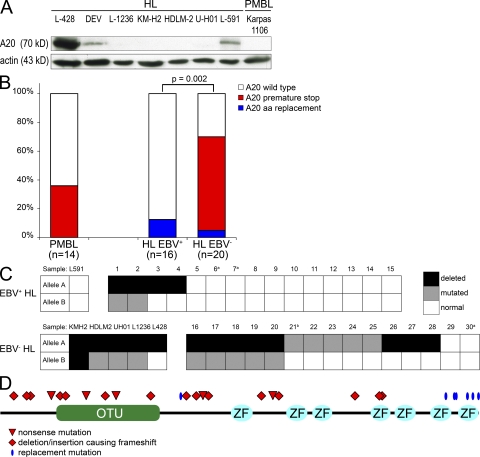
Figure 1.
Inactivation of A20 in cHL and PMBL. (A) Mutations in TNFAIP3 correlate with the absence of detectable A20 protein (∼70 kD) in lymphoma cell lines. Immunoblotting using anti-A20 antibody was performed with each 100 µg of whole-cell extracts of PMBL and HL cell lines. β-Actin was used as loading control. No truncated proteins were detected. (B) Frequency and pattern of TNFAIP3 mutations in PMBL and cHL arranged by EBV status (A20 wild-type: cases carrying exclusively wild-type TNFAIP3 sequence; A20 premature stop: cases with destructive mutations [nonsense mutations and deletions or insertions causing premature stop codons]; A20 missense: cases with missense mutations). Numbers in brackets indicate the numbers of cases analyzed. p-values were calculated using Fisher’s exact test. Case 19 harbors both missense and premature stop, and is depicted among the group with premature stop. (C) Graphic representation of allelic distribution of TNFAIP3 mutations of cHL grouped according to EBV status. The columns represent the cases, and the rows represent the two alleles. a, the loss of one allele cannot be excluded as cases were not evaluable by FISH and lacked heterozygous sequence polymorphisms; b, the case harbors two mutations, but their allelic distribution could not be determined. (D) Schematic representation of location of TNFAIP3 mutations translated to A20 protein in cHL and PMBL, as described in Tables I and II. OTU, ovarian tumor domain; ZF, A20 zinc finger domains.