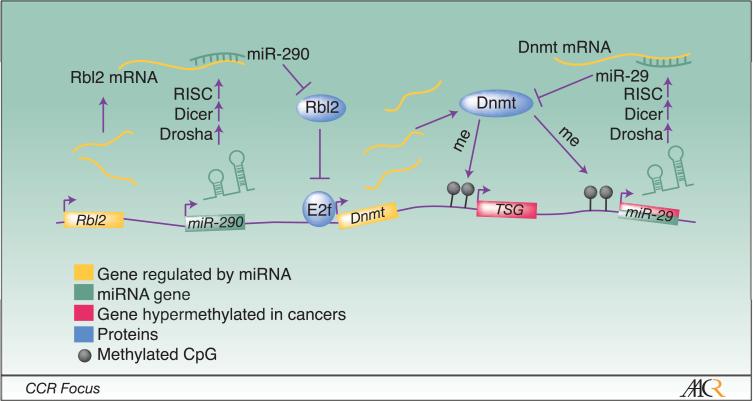
Figure 3. MicroRNAs (miRNAs) play a complex role in the regulation of genome-wide DNA methylation patterns.
Micro RNAs are ∼21 nucleotide single-stranded non-coding RNA molecules that are transcribed as a primary microRNA (pri-miRNA) transcript before undergoing two processing events by Drosha and Dicer. The mature miRNA interacts with the RNA-induced silencing complex (RISC) which can mediate both translational repression and mRNA transcript cleavage depending on the extent of homology between the miRNA and its target. At least two families of miRNAs affect the expression of DNMTs. The miR-290 family stimulates DNMT expression by targeting Rbl2, a retinoblastoma family protein that represses E2F-mediated activation of the DNMT genes. In contrast, the miR-29 family directly represses DNMT3A and DNMT3B transcripts. However, in cancer cells, the miR-29 locus is hypermethylated leading to transcriptional silencing of miR-29 and elevated expression of DNMT3A and DNMT3B.