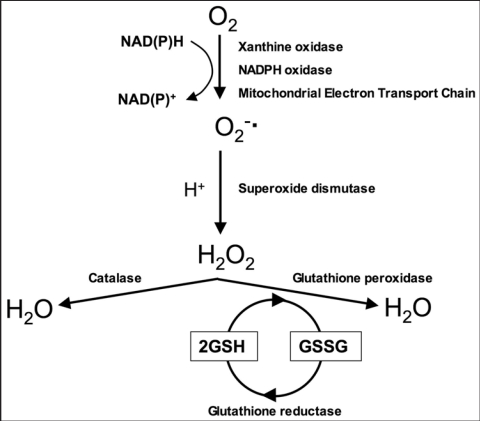
Figure 1.
Major pathways of reactive oxygen species generation and metabolism. Superoxide can be generated by specialized enzymes, such as the xanthine or NADPH oxidases, or as a by-product of cellular metabolism, particularly the mitochondrial electron transport chain. Superoxide dismutase then converts the superoxide to hydrogen peroxide which has to be rapidly removed from the system. This is generally achieved by catalase or peroxidases, such as the glutathione peroxidases which use reduced glutathione (GSH) as the electron donor.