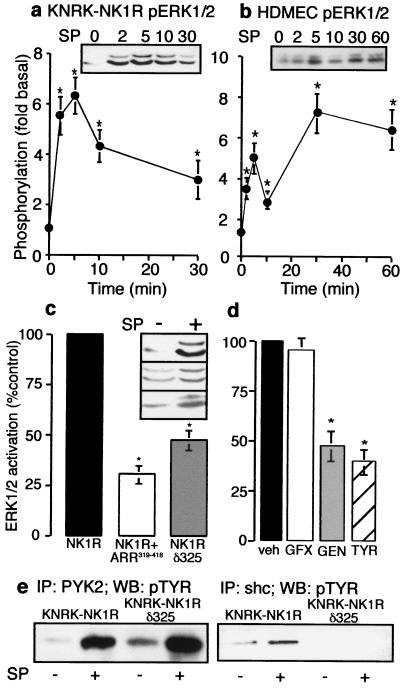
Figure 1.
NK1R-mediated activation of ERK1/2. (a and b) Cells were incubated with 10 nM SP (KNRK) or 100 nM [Sar9MetO211]SP (SM-SP, HDMEC) for 0–60 min. Phosphorylation of ERK1/2 in KNRK-NK1R cells (a) and HDMEC cells (b). (Inset) representative pERK Western blot. *, P < 0.05, as compared with untreated controls, n = 4. (c) KNRK-NK1R, KNRK-NK1R + ARR319–418, and KNRK-NK1Rδ325 cells were treated with 10 nM SP for 5 min and pERK1/2 was determined. (Inset) pERK Western blots of untreated and SP-treated cells (Top, NK1R; Middle, NK1R+ARR319–418; Bottom, NK1R, δ325). *, P < 0.05 as compared with SP-treated KNRK-NK1R cells, n = 3. (d) KNRK-NK1R cells were treated with 10 nM SP for 5 min with vehicle for inhibitors (veh), or after pretreatment with 100 nM GF103209X (GFX), 20 μM genistein (GEN), or 20 μM tyrphostin 25 (TYR) for 20 min, and pERK1/2 was determined. *, P < 0.05 for cells treated with SP-treated controls, n = 3. (e) KNRK-NK1R and KNRK-NK1Rδ325 cells were treated with or without 10 nM SP for 5 min and immunoprecipitated with either PYK2 antibody (Left) or shc antibody (Right), followed by Western blotting with phosphotyrosine (pTYR) antibody.