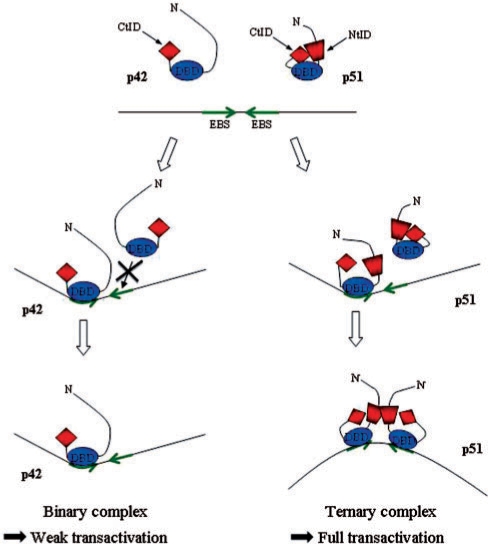
Figure 8.
Model for the differential regulation of the Stromelysin-1 promoter by p51 and p42 Ets-1 isoforms. The binding of one p42 molecule on the EBS palindrome (core consensus motifs in green) induced DNA minor groove bending. Two p42 molecules are unable to bind the EBS palindrome due to steric clashes between the two DBD domains (DBD, in blue). In contrast, two p51 are able to overcome these steric hindrances through a cooperative interaction leading to (i) a drastic rearrangement of the inhibitory module (CtID, red diamond and NtID, red trapezoid) and the creation of an intermolecular interface between the N-terminal inhibitory domains (NtID, red trapezoid) (ii) the induction of major DNA bending (opposite to the protein–DNA interface). This ternary complex, via the induced specific DNA curvature, is responsible for the full transactivation of the promoter.