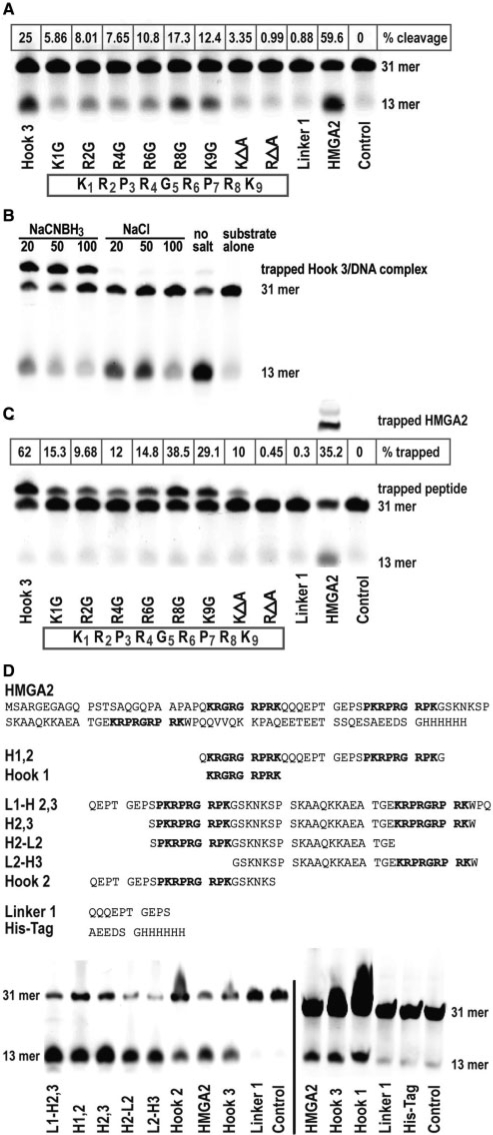
Figure 3.
Identification of nucleophiles in AT-hook 3. (A) Comparison of AP site cleavage activities of various hook 3 peptides with a linker peptide and full-length HMGA2. The hook 3 aa sequence with residues numbered is displayed in the box. The control reaction lacked any protein. The positions of the substrate (31-mer) and the cleavage product (13-mer) are indicated on the right side. The percentage cleavage was calculated based on the combined signal intensities from substrate and product (100%), after subtraction of the background value obtained with the control. (B and C) Trapping of peptides in a covalent intermediate complex with the 31-mer AP site substrate. Trapping conditions were first optimized in (B) with unmodified hook 3 and various concentrations of the trapping salt NaCNBH3, using NaCl as control. The percentage of trapped complexes was calculated in (C) based on the combined signal intensities from the 31-mer substrate and the shifted complex (100%), after subtraction of the background value obtained with the control. (D) Comparison of AP site cleavage activities of various peptides containing hook sequences. The aa sequences of full-length HMGA2 and of the peptides are shown on top of the cleavage assays. Note that we included two controls; a linker (Linker 1) and his-tag peptide.