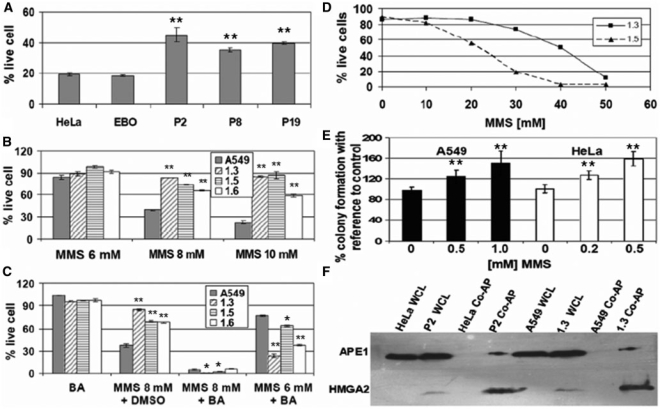
Figure 7.
HMGA2 expression confers resistance against MMS which can be reversed by co-treatment with the lyase inhibitor BA, and physical interaction of HMGA2 with APE 1. (A) Percentage of live cells determined by FACS after challenging HeLa cells and derivatives with 4 mM MMS for 1 h, followed by 48 h recovery. Data analyzed with Student's t-test. **P < 0.001. (B and C) Percentage of live cells determined by FACS after challenging A549 cells with MMS at the indicated concentrations for 1 h, followed by 48 h recovery. Data were normalized to untreated parental and transgenic cells (100%). BA was added to an additional set of wells during recovery, and DMSO, the solvent for BA, was added to a control set. Note that BA alone does not affect cell viability. Data analyzed with Student's t-test. *P < 0.005. **P < 0.001. (D) Percentage of live cells determined by FACS after challenging 1.3 and 1.5 cell lines with increasing concentration of MMS for 1 h, followed by 48 h recovery. (E) Percentage of surviving colonies from HMGA2-transfected cells upon treatment with MMS, with reference to cells transfected with control vector. Data analyzed with Student's t-test. **P < 0.001. (F) Western blotting analysis of co-affinity precipitation of cellular APE1 via HMGA2-His in transgenic cells (lanes 3, 4, 7 and 8). Whole cell lysates (wcl) were used as controls (lanes 1, 2, 5 and 6).