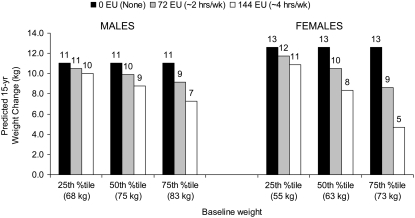
FIGURE 3.
Predicted cumulative weight change in men and women based on coefficients from the longitudinal, repeated-measures conditional regression model across 15 y of the Coronary Artery Risk Development in Young Adults (CARDIA) Study (n = 23,633 observations across 4995 individuals; 1985–1986 to 2000–2001). Sex-stratified, longitudinal, repeated-measures conditional regression model predicted annualized weight changes with control for total physical activity score (nonwalking), age, marital status, education (referent or ≥high school), smoking (referent or never smoked), and calorie intake; the interaction term was walking by baseline weight. Men: walking score of 144 (referent, 0), 25th percentile baseline weight for men (β = −0.07 kg/y; 95% CI: −0.23, 0.09; P = 0.4), 50th percentile baseline weight (β = −0.15 kg/y; 95% CI: −0.29, −0.02; P = 0.03), and 75th percentile baseline weight, BMI equivalent to overweight (β = −0.25 kg/y; 95% CI: −0.40, −0.10; P = 0.001). Women: 25th percentile baseline weight for women (β = −0.12 kg/y; 95% CI: −0.29, 0.05; P = 0.2), 50th percentile baseline weight (β = −0.28 kg/y; 95% CI: −0.43, −0.14; P = 0.001), and 75th percentile baseline weight, BMI equivalent to overweight (β = −0.53 kg/y; 95% CI: −0.68, −0.38; P < 0.001). Values may appear inconsistent because of rounding. Bars for 0 exercise units (EU) are identical across sex and baseline weight because of regression parameterization.