Figure 1.
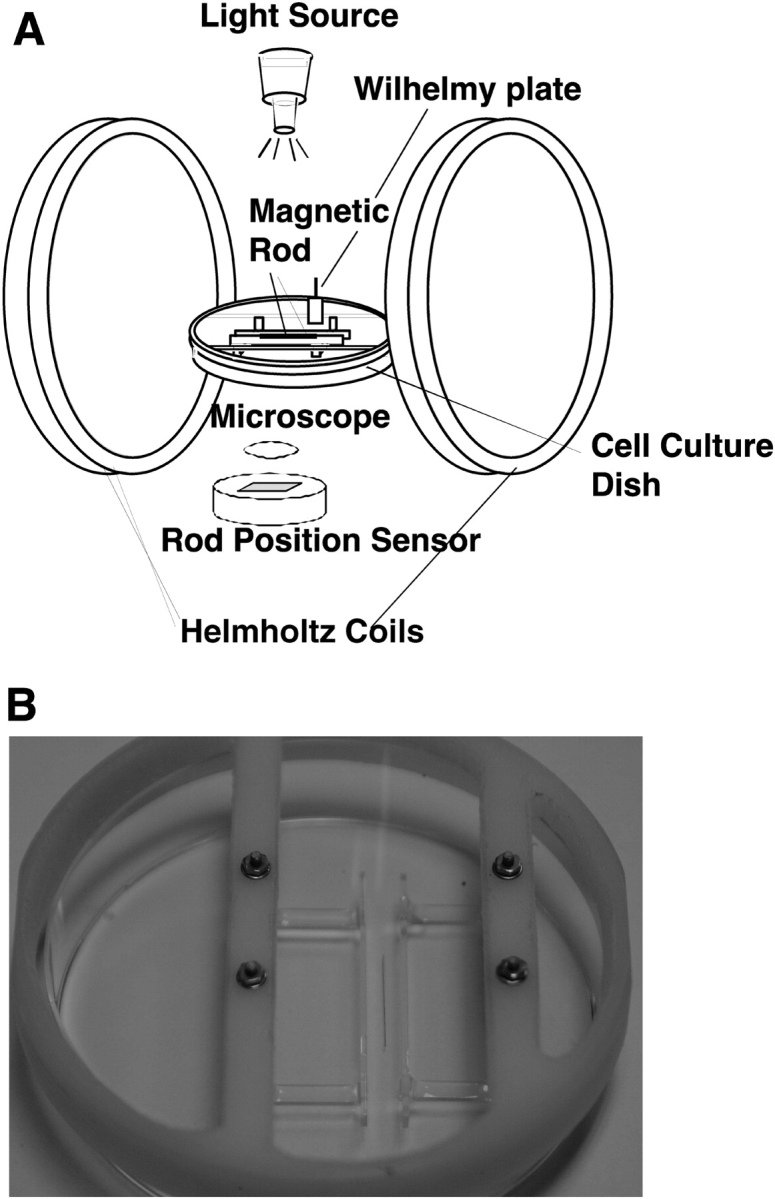
ISR used to measure lung surfactant rheology. (A) A surfactant monolayer is spread on a liquid subphase and surface pressure is continuously monitored by a Wilhelmy plate connected to a force transducer. A magnetized steel needle floating within the monolayer is displaced by varying the current delivered to the Helmholtz coils. By simultaneously monitoring the supplied current (oscillating applied shear stress) and resulting rod position (oscillating shear strain) as a function of time, rheological properties of the surfactant film are calculated. The interfacial storage modulus (Gs') is a measure of interfacial film elasticity and interfacial loss modulus (Gs”) is a measure of interfacial film viscosity. (B) An in situ cell for the ISR allows measurements of time-dependent changes in surfactant rheology to be conducted directly above a monolayer of cultured A549 epithelial cells.
