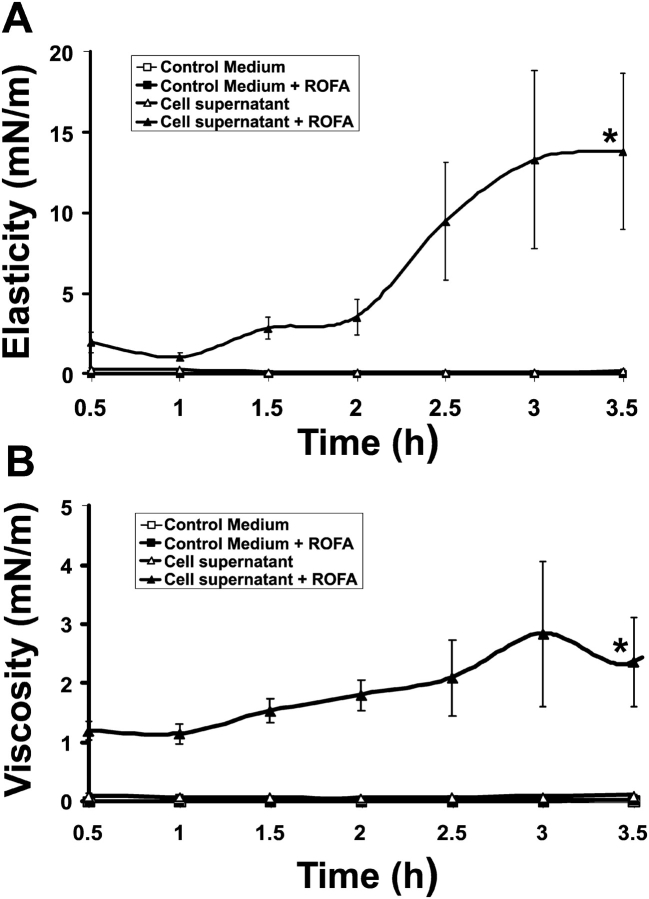
Figure 2.
Lung surfactant gelation is induced by ROFA-treated A549 AEC. Elastic storage modulus, Gs' (A) and viscous loss modulus, Gs” (B) are shown. A monolayer of lung surfactant spread on a subphase of DMEM media alone (open squares), or soluble ROFA (100 μg/ml) in DMEM (filled squares) shows very low elasticity (Gs') and viscosity (Gs”) representative of remarkable microfluidity. Conditioned supernatant from resting A549 AEC (open triangles) preserves the fluidity of lung surfactant. Conditioned media from ROFA-treated AEC (100 μg/ml for 16 h incubation) induces significant increases in elasticity and viscosity by 3.5 h, representing lung surfactant gelation (*P < 0.005, n = 3).